Written by
Yuri ZhangSummary: This post mystifies what services the Windows BitLocker feature provides including disk encryption and so forth, plus how to take advantage of them in real-life practice. Besides, iBoysoft DiskGeeker offers BitLocker in an efficient way.
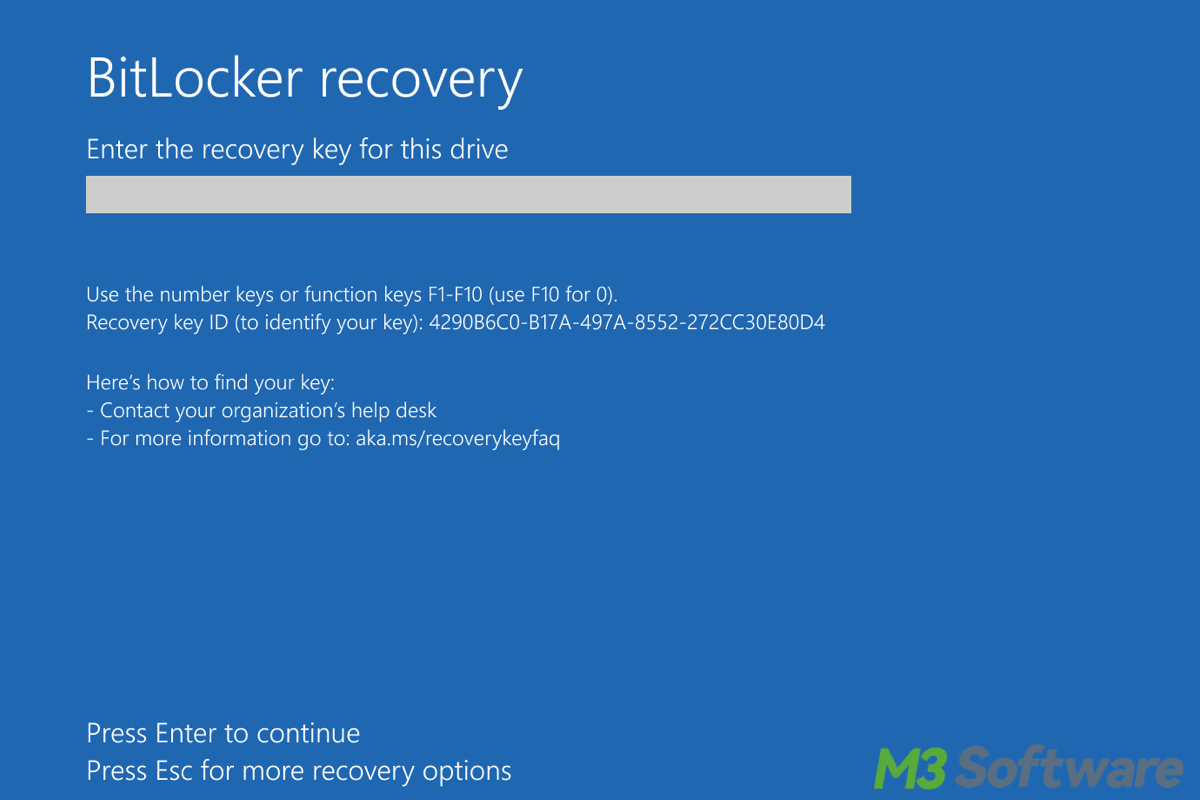
How can you keep your data safe if your device is lost or stolen? Windows BitLocker offers the answer by encrypting your entire drive whether you're using a personal laptop or managing enterprise devices.
Let's explore what service does the Windows BitLocker feature provide, and how BitLocker safeguards your data with simple, yet robust encryption.
What is BitLocker
The name, BitLocker comes from the combination of two words: "Bit" and "Locker". Bit refers to the fundamental unit of digital information in computing, representing a binary value of 0 or 1. In the context of BitLocker, it signifies the protection and encryption of the data at the level of individual bits or blocks of data on a disk.
Locker refers to the idea of a secure storage space, much like a physical locker, where you can store your valuable items. In this case, it represents the secure encryption of data on a hard drive, ensuring that unauthorized access is prevented. So, BitLocker essentially signifies a tool that "locks" (or encrypts) the data at the "bit" level to protect it from unauthorized access, providing full disk encryption for Windows operating systems.
Microsoft introduced it with Windows Vista as a security feature designed to safeguard data on computers, especially those used in corporate environments, from theft or exposure in case of loss or theft of the device. The name reflects the security function of the tool: locking (protecting) the data at its most fundamental level—bits of information.
What service does the Windows BitLocker feature provide?
The BitLocker feature in Windows provides full disk encryption to help protect your data by encrypting the contents of your hard drive or solid-state drive (SSD). The primary services and functions that BitLocker offers are as follows and you can see that they are correlated:
1. Full disk encryption and data protection
BitLocker encrypts the entire system drive (where Windows is installed) and any other selected drives, ensuring that all files on the drive are protected from unauthorized access. The primary goal of BitLocker is to protect sensitive data. If your device is lost, stolen, or accessed by unauthorized individuals, the encrypted data remains unreadable without the proper decryption key (PIN, password, or recovery key).
2. Pre-boot authentication
BitLocker can require pre-boot authentication (such as a PIN, password, or USB key) before the operating system starts. This means that even if someone removes the hard drive and tries to access the data from another machine, they cannot decrypt it without the authentication credentials.
3. Trusted Platform Module (TPM) integration
BitLocker works with the TPM (a hardware security module) to store the encryption keys securely. TPM helps ensure that the system boot process hasn't been tampered with, enhancing security by verifying the integrity of the system before allowing access to the data.
4. Encryption for non-system drives
In addition to the operating system drive, BitLocker can encrypt additional data drives (internal or external), such as secondary hard drives or USB drives. This feature is particularly useful for protecting external drives that store sensitive data.
5. Automatic unlock (for fixed drives)
For drives that are automatically unlocked (like a fixed internal drive), BitLocker can be set to automatically decrypt the drive once the system boots up and the user logs in. This is useful for users who do not want to manually unlock drives each time.
6. Recovery options
BitLocker provides several ways to recover encrypted data if the password is forgotten or if there is an issue with the system, refer to Forgot Your BitLocker Password? Here's How to Remedy It.
7. BitLocker To Go
This is an extension of BitLocker that allows you to encrypt removable drives (such as USB flash drives and external hard drives). When a drive is encrypted with BitLocker To Go, you can only access the data after entering the correct password on any system that supports BitLocker.
8. Management tools (for IT Admins)
BitLocker Management: Windows provides administrative tools (like BitLocker Drive Encryption in Control Panel and Group Policy) to manage encryption policies, configure startup options, and deploy BitLocker across multiple machines in an enterprise. Windows also offers command-line tools (such as manage-bde) to manage encryption and recovery options.
Note: BitLocker has a minimal impact on system performance, especially with modern hardware. It uses efficient encryption algorithms (such as AES) and can leverage the hardware acceleration in modern CPUs (e.g., Intel's AES-NI or AMD's equivalent) to ensure that encryption and decryption operations do not noticeably slow down the system.
How to take advantage of BitLocker services
Correspondingly, how do we employ the above features and practice them in real life? Here's a breakdown of how to enable and use BitLocker, along with an explanation of each feature, button, and operation:
1. Accessing BitLocker settings
- Open Control Panel (you can search for it in the Start menu).
- Navigate to System and Security > BitLocker Drive Encryption.
- Alternatively, you can search for BitLocker in the Start menu and click on Manage BitLocker.
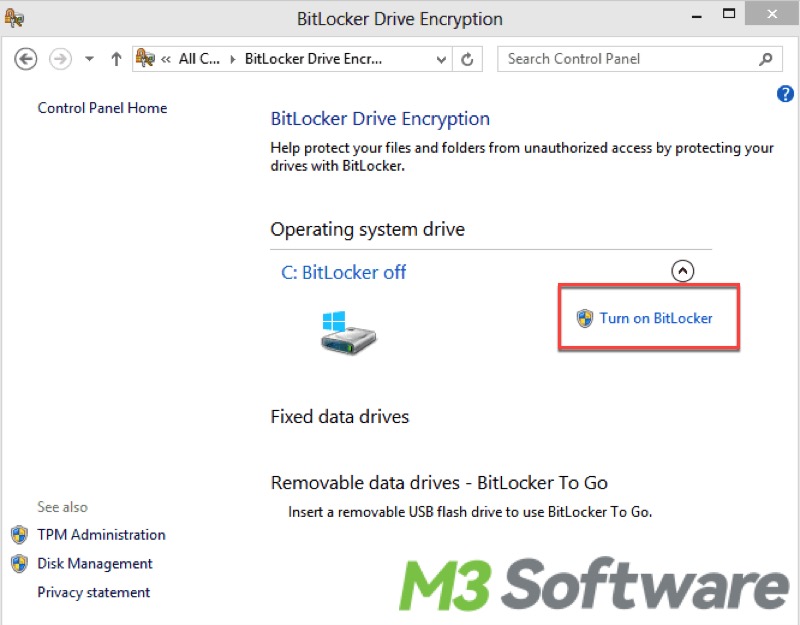
2. Turning on BitLocker
- Under BitLocker Drive Encryption, you will see a list of available drives.
- Find the drive you want to encrypt (usually the C: drive for the operating system) and click Turn on BitLocker next to it.
If you don't see this option, it could be due to your device lacks a TPM (Trusted Platform Module) chip (for system drives), or the drive is not formatted with NTFS or is a removable drive.
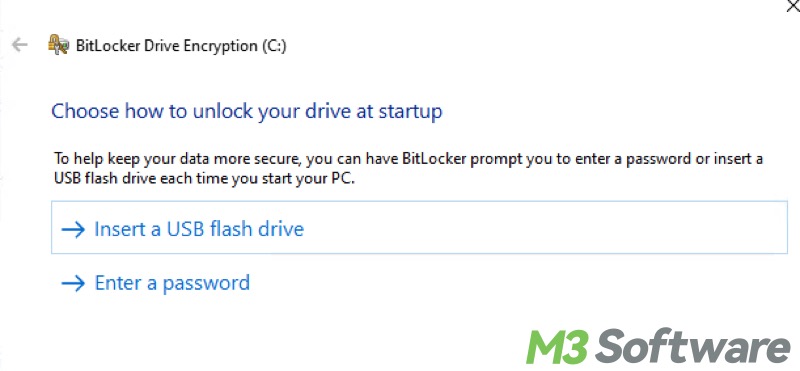
3. Choosing how to unlock the drive
When it comes to pre-boot authentication: BitLocker will ask how you want to unlock the drive at startup. You have several options:
- Use a password: Enter a strong password that you'll need to input each time the computer starts.
- Use a smart card: If your computer supports it, you can choose to unlock the drive using a smart card.
- Use a PIN: With TPM, you can also use a PIN (numerical passcode) to unlock the system drive.
- Use a USB flash drive: You can use a USB drive with a recovery key as the unlocking method.
4. Saving the recovery key
BitLocker will ask you to choose how you want to save or back up your recovery key:
- Save to a Microsoft account (cloud storage).
- Save to a file (save the recovery key as a .txt file on an external drive).
- Print the recovery key (print it on paper).
- Save to USB drive.
The recovery key is essential if you forget the password or PIN, or if the TPM becomes inaccessible.
5. Choosing the encryption mode
- Encrypt used disk space only: This option will encrypt only the portions of the drive that are actively in use (recommended for faster encryption, especially on new drives).
- Encrypt the entire drive: This option will encrypt the entire drive, including free space. This is recommended for existing drives or when you want maximum security.
Share this and let more people know about this incredible Windows built-in feature.
6. Start encryption or decryption
After selecting all your preferences, click Start encrypting. Encryption may take a while depending on the size of the drive and the amount of data stored. You can continue using your computer while BitLocker encrypts in the background, but performance may be slightly slower. Decryption is also supported here.
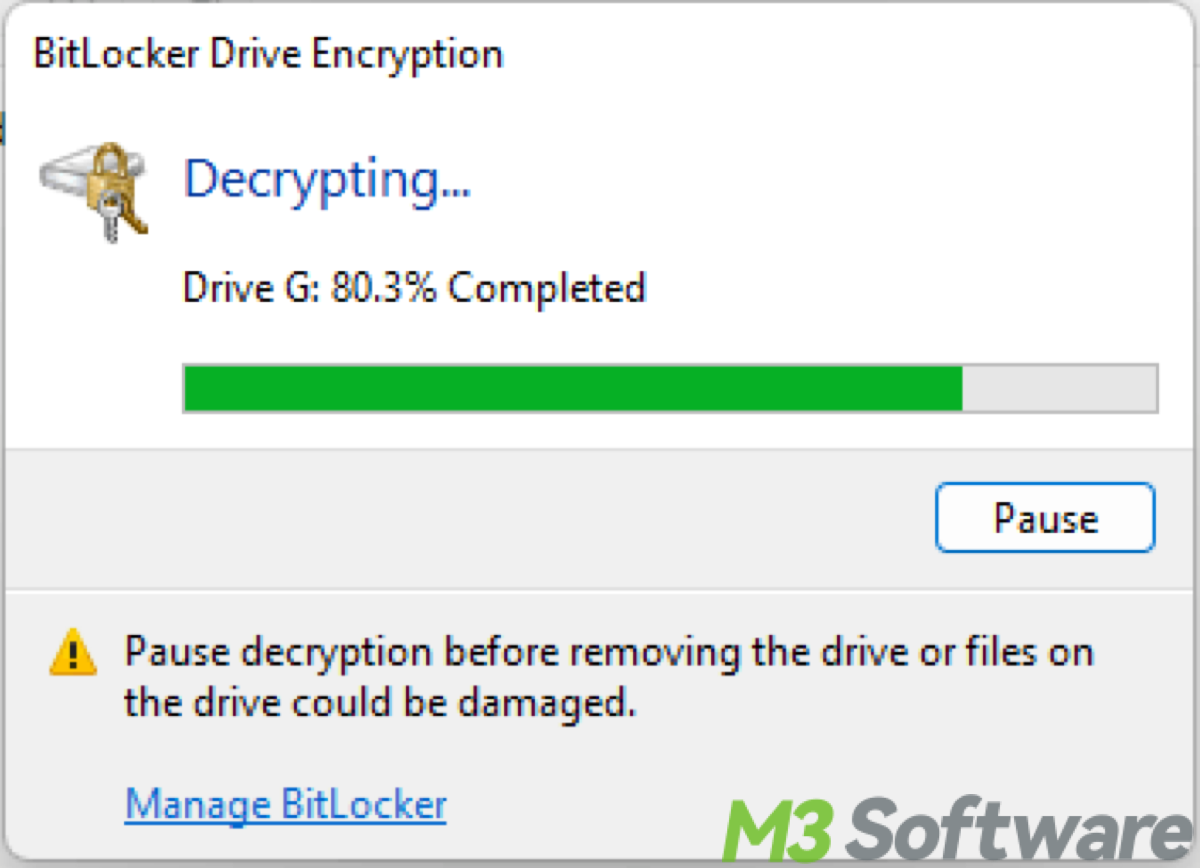
Tips: The progress of encryption is visible via the BitLocker Drive Encryption window in Control Panel. You can see how much of the drive has been encrypted and whether it is in the process of being encrypted.
7. Managing BitLocker while enabled
If you need to change settings after enabling BitLocker:
- Control Panel > BitLocker Drive Encryption: You can manage the drive's settings, including turning off BitLocker, changing the password, or adding a smart card for authentication.
- Suspend BitLocker: Temporarily disables BitLocker encryption without decrypting the drive, often used for maintenance tasks (e.g., firmware updates). It will automatically resume after reboot unless manually disabled.
- Turn off BitLocker: If you no longer need encryption on the drive, you can turn it off. This will decrypt the entire drive.
8. BitLocker To Go for removable drives
- When inserting a USB drive, you can right-click on it in File Explorer and select Turn on BitLocker.
- You'll be prompted to choose a password for the drive and to decide how to save the recovery key.
- After the encryption process finishes, the drive will require the password or other authentication methods each time it is connected to a computer.
9. Advanced BitLocker options (through Group Policy or Command Line)
Administrators can set advanced BitLocker settings using Group Policy Editor (for Windows Pro, Enterprise, or Education editions):
- Open the Local Group Policy Editor by typing gpedit.msc in the Start menu.
- Navigate to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > BitLocker Drive Encryption.
- Here you can configure various options like forcing the use of a PIN, requiring the TPM, and configuring the recovery key settings.
manage-bde is the command-line tool for managing BitLocker, here are some common commands for your reference:
- Check status: manage-bde -status
- Turn on BitLocker: manage-bde -on C:
- Suspend encryption: manage-bde -protectors -disable C:
- Unlock a drive: manage-bde -unlock C: -Password
10. BitLocker Recovery Environment(WinRE)
If BitLocker prevents booting (due to issues like changing hardware or BIOS settings), you may need to use the BitLocker Recovery Environment. At boot, you may be prompted for the recovery key. You can either type it in manually or use a recovery USB key. You can refer to How to Exit BitLocker Recovery Loop Under WinRE.
Conclusion
To sum up, BitLocker, as its name suggests, 'locks' your files to protect your data from unauthorized invasion, assuring us that our privacy is guarded. Following the above guidance, you can make the best use of services homed to BitLocker.
BitLocker provides beefy protection for data by encrypting entire drives and preventing unauthorized access, even if the device is physically compromised. It integrates with security features like TPM, supports multiple authentication methods, and offers recovery options, making it an important tool for data security, particularly for enterprises or individuals with sensitive information.
Spread this and become a facilitator in cyberspace.
