Written by
Yuri ZhangSummary: This post illustrates what the Disk tab in Task Manager reveals, what each metric (eg., disk usage, disk active time ) means, and how you can use this data to maintain or improve system performance.
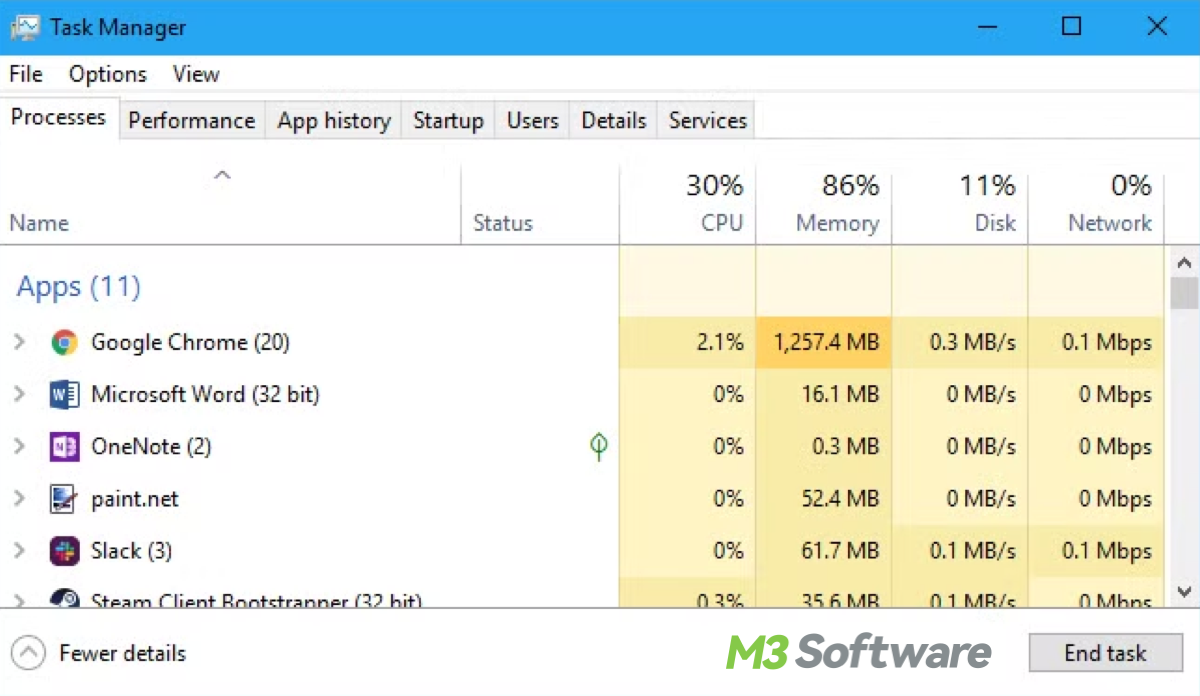
As time goes by, Windows devices may get stuck at certain screens if we use them carelessly by adding heaps of programs, applications, and files. It's not weird to think about ending the problematic task.
But how, this is where the Task Manager comes in handy when we are fixing slow system performance, the Disk tab provides ins and outs about how your storage devices are being used.
You can open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc. Now let's explore what Disk in Task Manager means, what metrics in it should we pay attention to, and how to read them.
What does the Disk tab show in Task Manager?
The Disk tab in Task Manager provides a detailed view of how your PC's storage devices (Hard Disk Drives (HDD) or Solid State Drives (SSD)) are performing.

Note: The Disk column in the Processes tab shows which processes are using the disk and how much disk space each process consumes. This helps you to identify which applications or system processes are causing high disk usage so as to enhance PC performance.
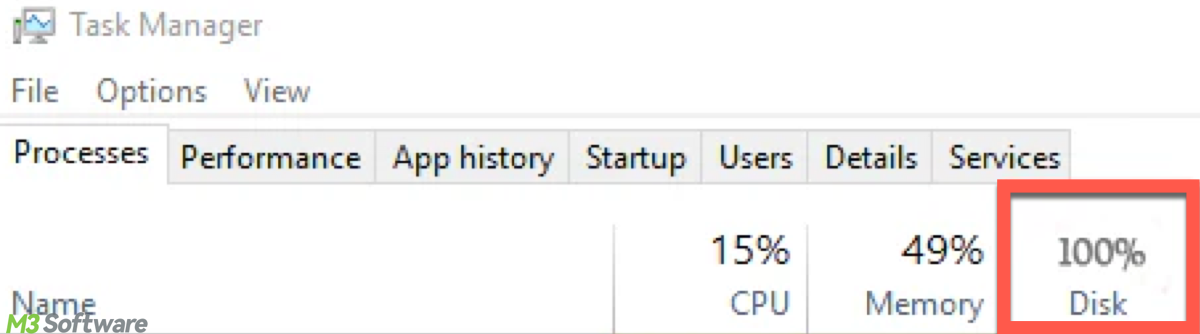
Disk Usage (%)
This metric shows the percentage of your disk's capacity that is being used at any given moment. If the percentage is high, such as 100%, it means your disk is fully utilized, which can result in system slowdowns.
Read/Write Speed
The Read/Write Speed columns show the amount of data being read from or written to the disk, measured in megabytes per second (MB/s).
A high read or write speed usually indicates that data-heavy processes are running, such as file transfers, video rendering, or system updates.
While this can be normal, excessively high speeds sustained over long periods can slow down your system if not managed properly.
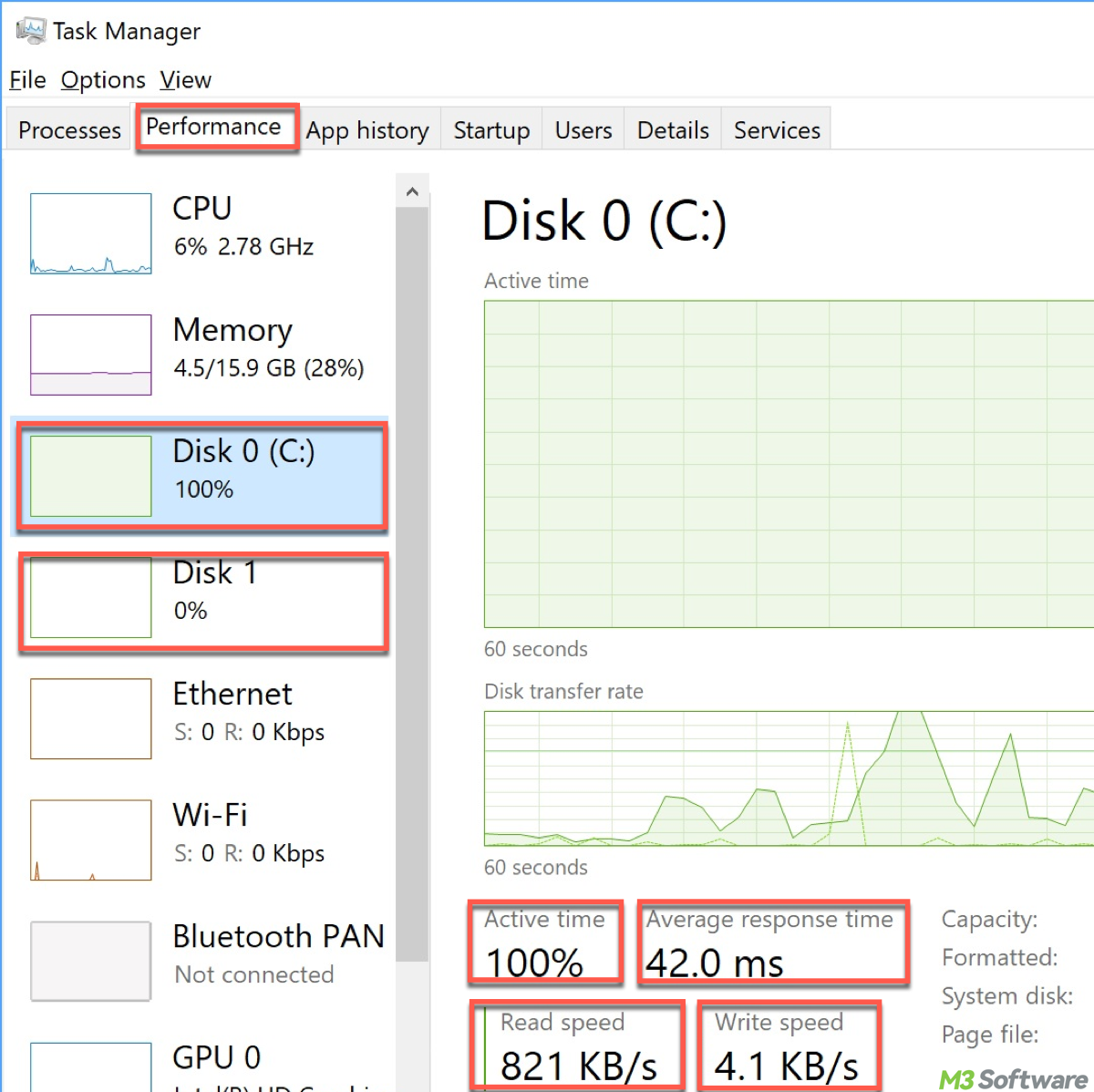
Disk 0, Disk 1, etc.
If your system has more than one storage device, you'll see each one listed separately (e.g., Disk 0, Disk 1, etc.). Disk 0 is typically your system drive, where the operating system (OS) is installed, and it's the most crucial disk for overall system performance. Monitoring this disk is important, as its performance directly affects the responsiveness of your computer.
Disk Active Time (%)
Disk Active Time shows how much time the disk spends actively processing read/write requests. For example, a Disk Active Time of 100% means the disk is actively working to fulfill requests the entire time it is being used. A high active time combined with high disk usage can indicate that your disk is under stress, which could lead to slower performance.
Response Time
Response Time measures how long it takes for the disk to respond to a request. High response times can indicate that the disk is struggling to keep up with demand, which may lead to delays or lag when accessing files or launching applications.
Share this and continue to dissect these features.
How to troubleshoot Disk issues in Task Manager
If you're experiencing system slowdowns and suspect that your disk might be the culprit, you can use the Disk tab in Task Manager to identify the issue:
- Go to the Processes tab in Task Manager and check the Disk column to see which applications are consuming the most disk resources. If an application is consuming too much disk space, try closing it to free up resources.
- Keep an eye on Disk Active Time and Disk Usage. If both are consistently high (especially near 100%), it might indicate that your disk is being overworked. This could be a sign of either resource-heavy tasks or a need for better disk optimization.
- If your system disk (typically Disk 0) is near full capacity, you might experience slowdowns. Use Disk Cleanup or remove unnecessary files to free up space. If your disk is close to its maximum capacity, this can lead to performance degradation.
- Some programs automatically start when your system boots up and consumes disk resources. You can manage them in Task Manager by going to the Startup tab and disabling non-essential applications.
Other than these, iBoysoft DiskGeeker for Windows is visually pleasing with fabulous functions. It analyzes disk space to clean up junk files or large files, and securely erase data from disks. It also tests disk speed and adjusts partition sizes. Click the following green button to have optimal disk management.
Conclusion
Disk metrics are interlinked and reveal storage device performance. High Disk Usage with high Disk Active Time indicates a heavy load, causing lag or freezing.
100% disk usage suggests full capacity, leading to slowdowns from updates or background tasks. Extended High Disk Active Time can signal a bottleneck, causing lag even if other resources aren't heavily used.
Whether it's large files, background processes, or a full disk, Task Manager helps you pinpoint what's causing the strain on your system. Regularly checking your disk's performance can keep your system running efficiently.
Share and channel these words into action.
