Written by
Yuri ZhangSummary: This article defines memory.dmp consisting of its location and specific types, explains why we should delete it on Windows devices. Note that iBoysoft DiskGeeker helps filter memory.dmp.
Some memories are precious and positive, some are traumatic and superfluous, which we should discard. This is why we have memory.dmp and why we should dump certain kinds of memory.
Technically, the memory.dmp file contains a snapshot of the system's physical memory (RAM) at the time of the crash and can be used for debugging and diagnosing the cause of the system crash. Let's explore memory.dmp's definition and whereabouts.
What is memory.dmp?
Memory.dmp is a memory dump file created by the Windows operating system during a critical system failure, such as a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), and a system crash.
If you keep an eye on industry information, you'll find memory.dmp made some sense when the latest widespread issue of blue screens occurred among the Windows users.
The file contains a snapshot of the system's memory at the moment of failure, capturing information such as running processes, data, and the state of system operations.
Note: The purpose of the memory.dmp file is to provide an in-depth snapshot of the system's memory state during a crash. This helps pinpointing the underlying cause of system failures, which could be linked to hardware issues, software conflicts, driver problems, or other critical errors.
However, as an average user instead of developer or administrator, the large space memory.dmp occupied seems burdensome, and it will be generated later on. We can choose to sift & clean it swiftly through iBoysoft DiskGeeker for Windows without the toil of searching & waiting in File Explorer. It implies it's safe to delete memory.dmp.
Share this feat tool and help those who have no idea of memory.dmp.
Location of memory.dmp file
By default, the memory.dmp file is stored in the root directory of the system drive (usually C:\), in a folder called Windows under C:\Windows\memory.dmp. However, it could also be located in a different folder if you have configured Windows to save the dump file elsewhere, which we usually don't do that.
Types of memory dumps
There are different types of memory dumps that Windows can generate during a crash:
| Memory Dump Type | Location | Size | Content | Usage |
| Complete Memory Dump | C:\Windows\memory.dmp (or another path if SystemRoot is changed) | Large (several GB) | Entire system memory (user-mode and kernel-mode) | Deep system crash analysis and debugging |
| Kernel Memory Dump | C:\Windows\memory.dmp | Medium (100s MB) | Kernel memory (excluding user-mode) | Debugging kernel-level issues |
| Small Memory Dump (Minidump) | C:\Windows\Minidump\ | Small (256 KB) | Error codes, stack trace, loaded drivers | Quick crash analysis |
| Automatic Memory Dump | C:\Windows\memory.dmp | Medium (similar to kernel dump) | Kernel memory, automatically managed by Windows | Default memory dump for system crashes |
Note: The SystemRoot\memory.dmp file in Windows refers to the full memory dump file created by Windows during a system crash. SystemRoot is an environment variable in Windows that points to the folder where the Windows operating system is installed (typically C:\Windows).
Necessity to clean memory.dmp file and how
The memory.dmp file can be quite large, especially for systems with large amounts of RAM. A complete memory dump may be several gigabytes in size. Due to this, it can take up significant disk space, particularly on systems with limited and accumulating storage capacity.
If the system is low on disk space, or if the file is no longer needed for troubleshooting, the memory.dmp file can be deleted. iBoysoft DiskGeeker can analyze large files to optimize your disk space usage and make room for incoming files.
Tutorial to use iBoysoft DiskGeeker for dealing with large files:
Step 1: Click the following green button to download iBoysoft DiskGeeker and launch it.
Step 2: Tap into "Search for large files" from the Space analyzer module.
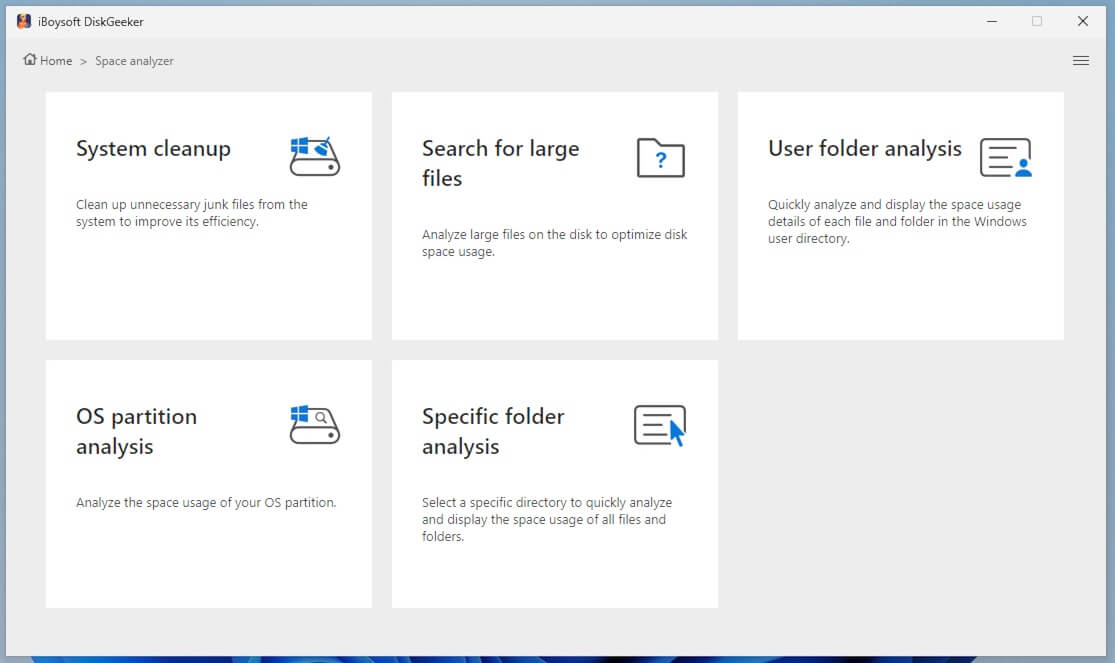
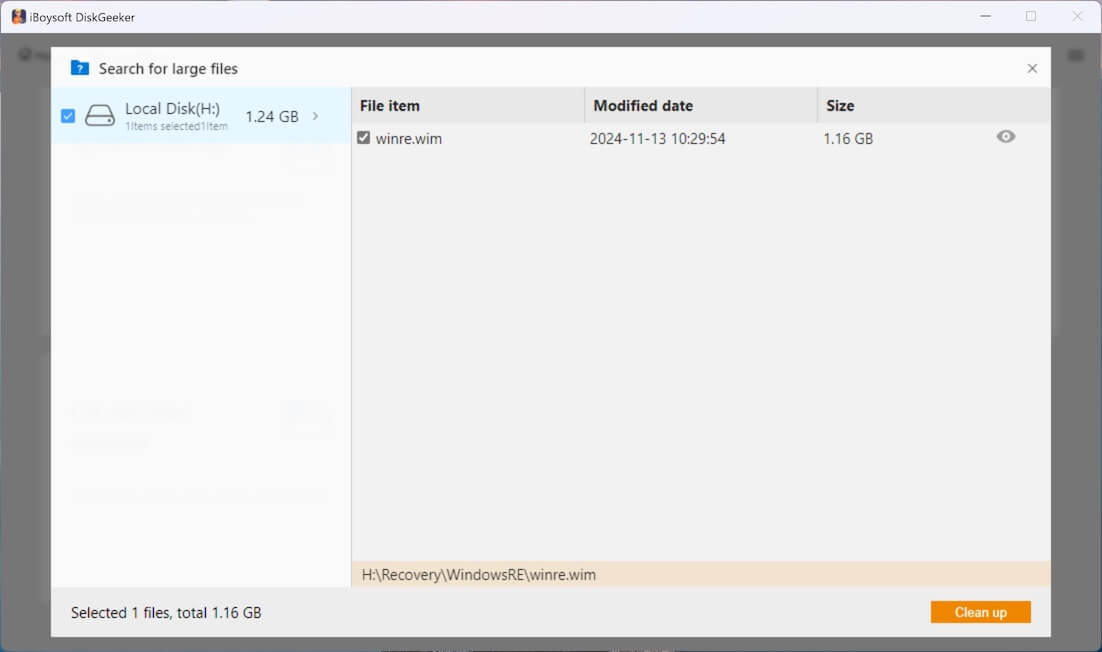
Step 3: Select a Partition to scan for large files so that you can screen out the memory.dmp file breezily.
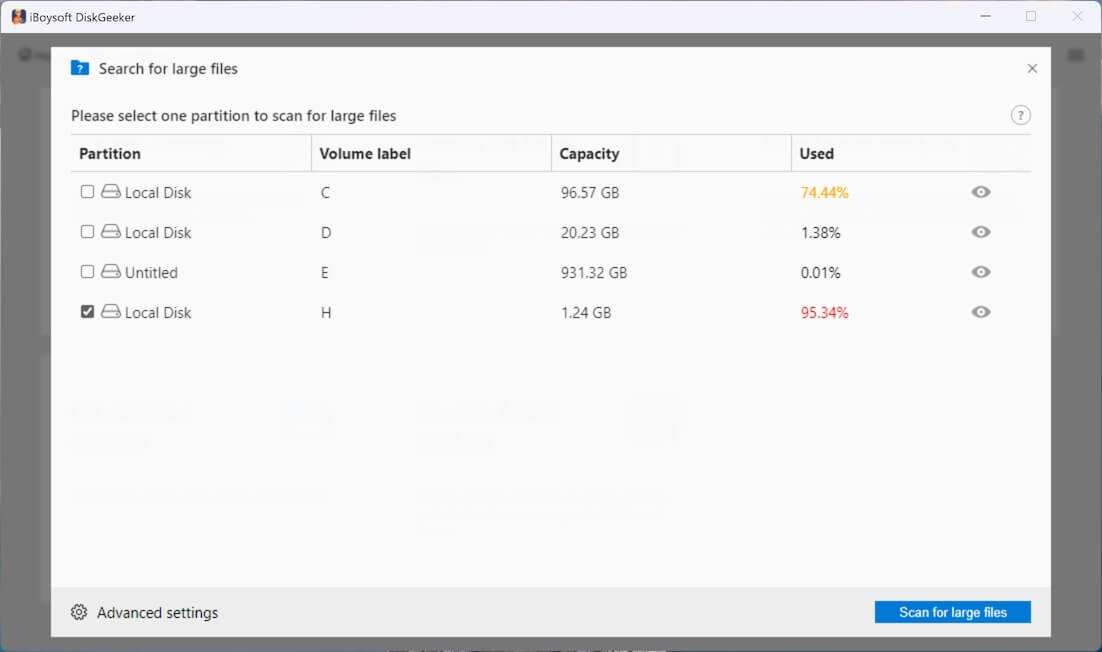
For the initial large file searching, you need to go to "Advanced settings" at the bottom left corner to set the minimum file size for scanning. Here, you can also add the file extension to prevent the tool from searching for certain files.
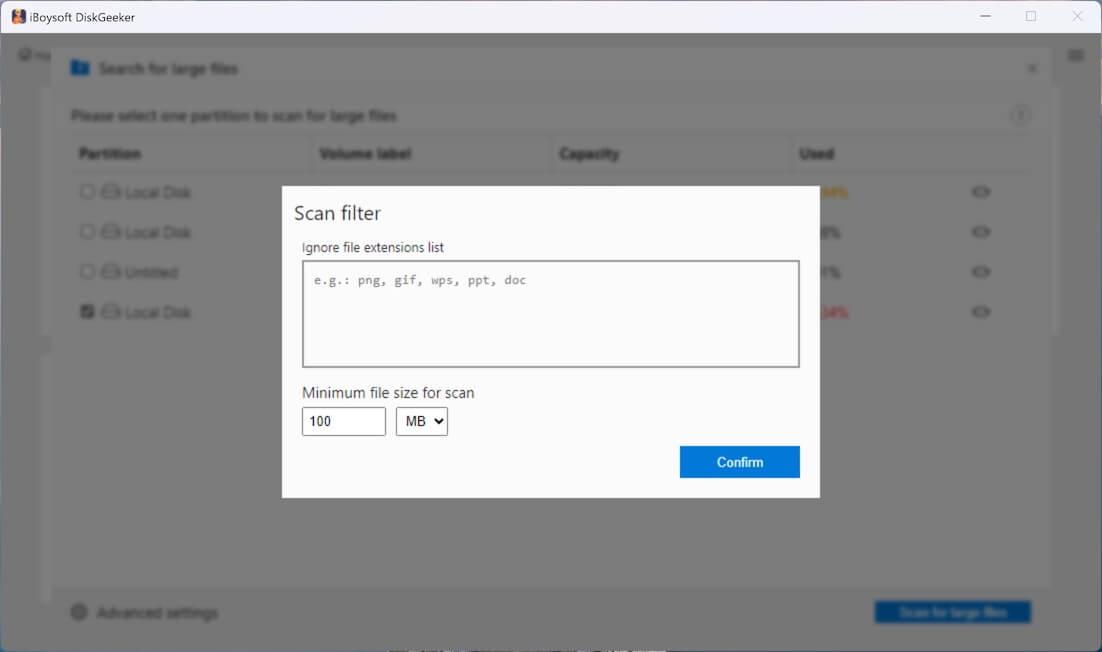
Step 4: Click "Search for large files" to start scanning.
Step 5: Choose what you want to delete, and click "Clean up."
Good news, you can click the view button to check the memory.dmp file or other searched large files before deletion.
Related articles:
Easily Find and Organize Your Downloaded Files in Windows
File Name Extensions Showcase Skills in Windows 11/10/8/7
Recognize the Power of BitLocker Folder and Drive Protection
Glad to grab your enormously valuable attention, don't be stingy to share.
