Written by
Yuri ZhangSummary: This article breaks down how to remove a directory/file/folder in Windows 10/11 even forcefully including File Explorer, Command Prompt, PowerShell, Safe Mode, and iBoysoft DiskGeeker for Windows.
Deleting folders, directories, or files in Windows 10/11 is usually a simple task. However, sometimes Windows doesn't allow you to delete certain items due to issues like files being in use, permission problems, or system protection.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll walk you through how to delete folders, directories, and files on Windows 10/11 in both normal and forceful ways, and explain when each method is appropriate. If there's a stubborn file that cannot be deleted, please refer to: (6 Ways) Delete Files That Cannot Be Deleted on Windows 11
Better still, the iBoysoft Disk Windows Geeker for Windows is compatible with all the deletion processes by providing a detailed overview of your disk space usage and making it easier to identify and remove batch redundant or unnecessary files.
How to remove a directory/file/folder in Windows10/11 with normal methods
The normal delete process is the simplest and safest way to remove files, folders, or directories. In this section, we'll focus on basic deletion methods that work for most scenarios.
1. Delete via File Explorer
The most common and easiest method to delete a file or folder is via File Explorer. You may be interested in how to select multiple files in Windows
- Open File Explorer (or press Windows key + E).
- Navigate to the file or folder you want to delete.
- Right-click the file or folder and select Delete, or select the item and press the Delete key on your keyboard.
- The item has been moved to the recycle bin. To permanently delete, right-click the Recycle Bin and select Empty Recycle Bin.
This method works well when there are no system processes or permissions issues preventing deletion. It is ideal for personal files and folders not protected by Windows or running applications.
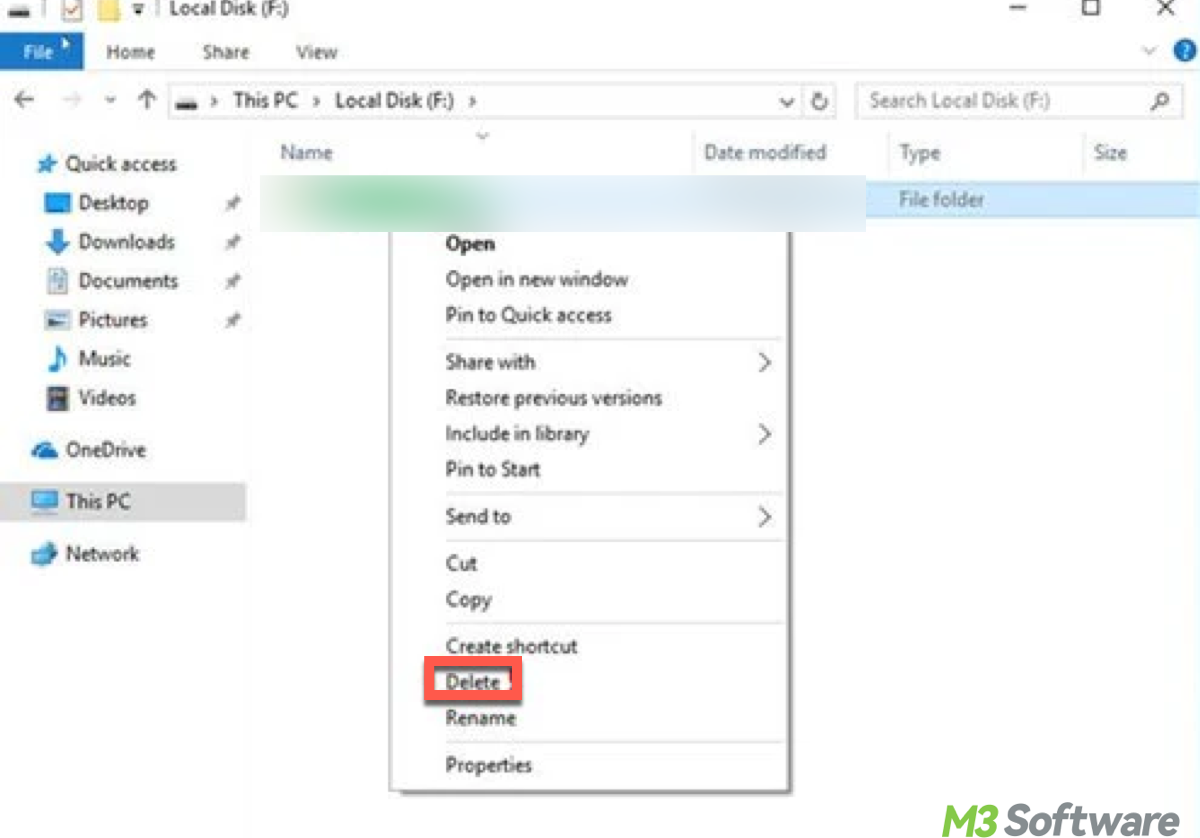
2. Delete via the Context Menu (Shift + Delete)
If you want to skip the Recycle Bin and permanently delete a file or folder, you can use Shift + Delete.
- Select the file or folder you want to delete.
- Hold the Shift key and press Delete on your keyboard.
- You'll be asked for confirmation. Click Yes to permanently delete it.
Use this when you are sure you no longer need the file or folder, and you don't want it to be saved in the Recycle Bin. It is great for larger files that might take up too much space in the Recycle Bin.
3. Delete files in Windows via Command Prompt
The Command Prompt offers a way to delete files through commands, which can be more efficient when managing large numbers of files or dealing with files in difficult-to-access locations.
- Type cmd in the search bar, right-click it, and select Run as Administrator to open Command Prompt.
- Type the following command(C:\path\to\file specifies the path to the file you want to delete. You should replace "C:\path\to\file" with the actual path to the file you want to remove):del "C:\path\to\file"
- Press Enter to delete the file.
Use this when deleting files from a location that is difficult to access through File Explorer, such as system folders or deep subdirectories. It is good for scripting or batch deletion of multiple files.
Share this and go ahead to help others with deleting problems on their computer.
How to remove a directory/file/folder in Windows10/11 with forceful methods
Sometimes, the normal delete methods fail, for instance, how to delete a file in Windows that won't delete/when access is denied. You need to use more advanced or forceful techniques to remove stubborn files or folders. These methods are useful when files or folders are locked by a process, have system-level permissions, or are in use by another program.
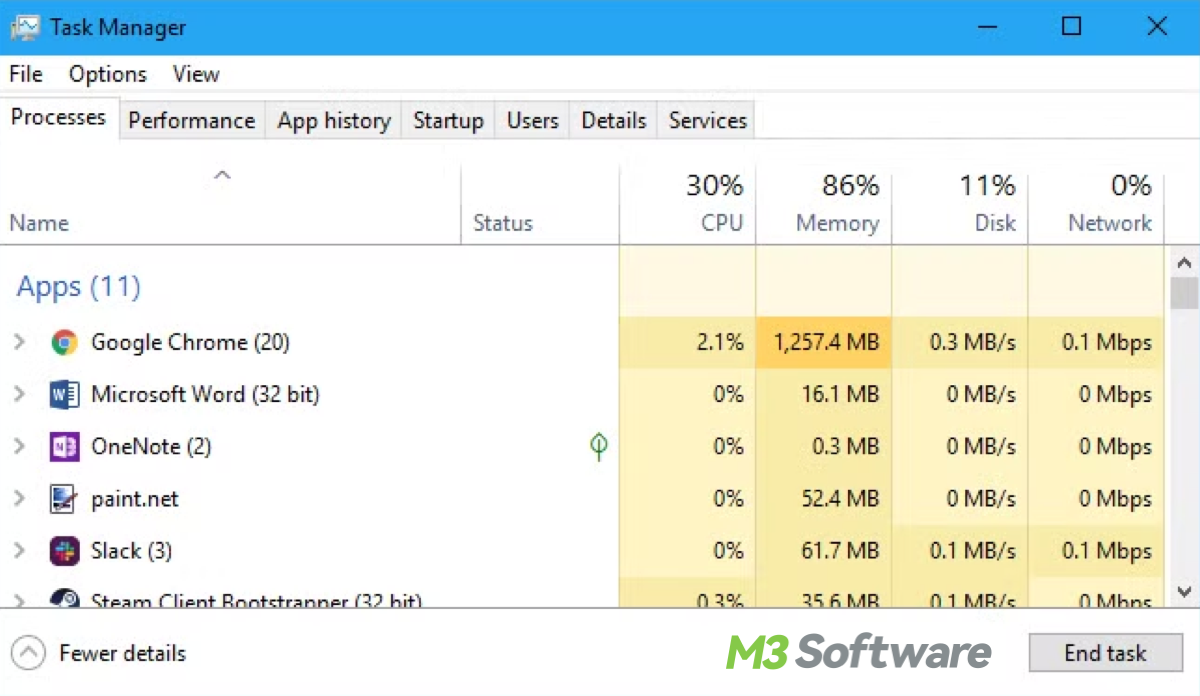
1. Use Task Manager to end processes (unlock files)
If a file or folder is locked because it's being used by a process, closing the program or process can free it up for deletion.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
- Look for any processes that may be using the file or folder such as Microsoft Word or Excel.
- Right-click the process and select End Task.
- After ending the task, attempt to delete the folder or file again
When a file or folder is locked by a program or process. It is effective for preventing deletion errors caused by files in use.
2. Delete files/folders in Windows via Command Prompt (forceful deletion)
If a folder or file is stubborn and won't delete through File Explorer, using Command Prompt with the rmdir (for folders) or del (for files) commands can force deletion.
- Type cmd in the search bar, right-click it, and select Run as Administrator to open Command Prompt.
- Use the following command to delete a folder and all its contents:rmdir /s /f "C:\path\to\folder"
- Use the following command to forcefully delete a file:del /f /q "C:\path\to\file"
Note: In the above commands, /s means deleting all files and subdirectories in the folder. /f means forceful deletion, even for read-only files. /q means quiet mode, aka no confirmation prompts.
Use this method when you cannot delete a folder or file through File Explorer due to it being locked, read-only, or in use. It is suitable for system-level folders or files that are difficult to delete normally.
3. Delete files/folders in Windows with PowerShell (forceful deletion)
PowerShell is another tool that provides advanced commands for managing files and folders, including the ability to forcefully remove stubborn items.
- Right-click Start, and select Windows PowerShell (Admin) to open PowerShell as Administrator.
- To delete a folder, type the following cmdlet (Recurse indicates deleting all contents inside the folder):Remove-Item "C:\path\to\folder" -Recurse -Force
Use this method when you want to delete a folder or file with advanced options or scripting or deal with files or folders that are not responding to traditional deletion methods.
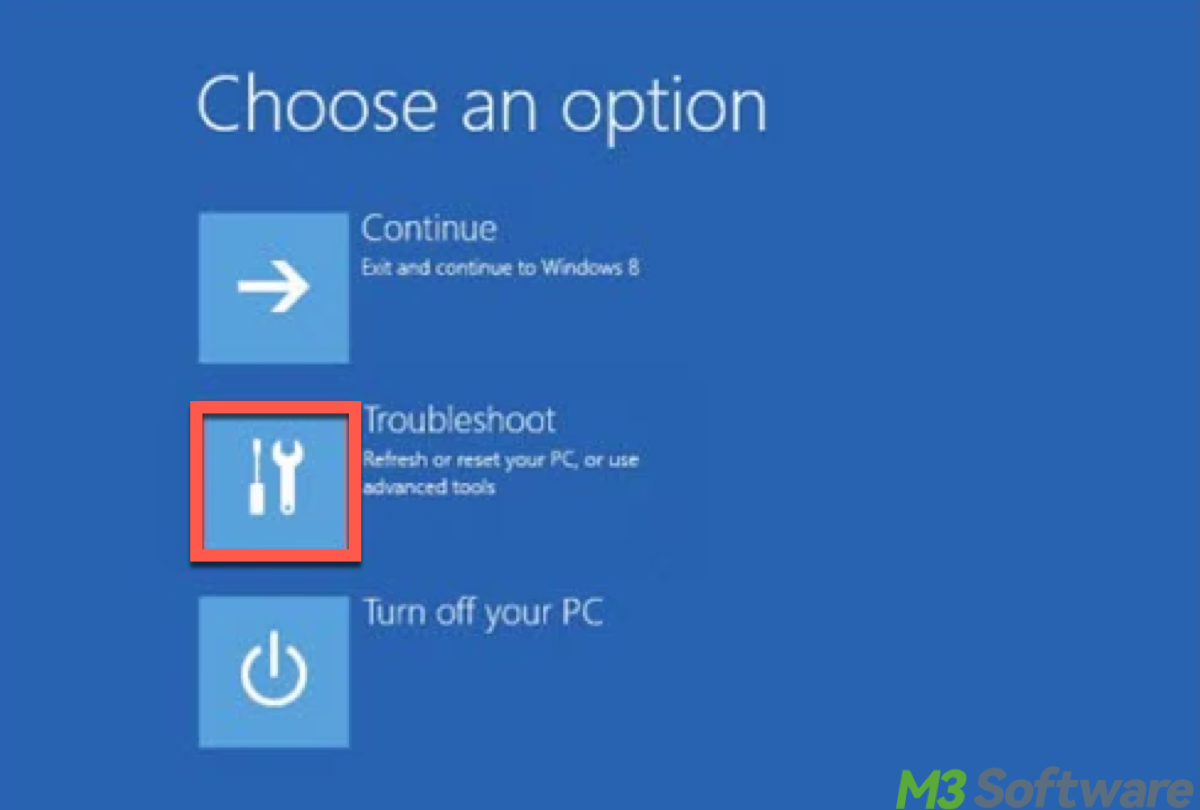
Bonus tip: boot into Safe Mode
In Safe Mode, Windows only loads essential drivers and processes, which can help bypass any system-level locks that are preventing deletion.
- Hold down the Shift key and click Restart from the Start menu to access Advanced Startup Options.
- Select Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > Startup Settings > Restart.
- Once your PC restarts, press 4 or F4 to boot into Safe Mode.
- Try deleting the folder or file again.
This approach is ideal when you are unable to delete a folder because it's being locked by a system process or a background application and is useful for deleting stubborn files that are protected or in use.
Tips: When all else fails, third-party tools like Unlocker or LockHunter can help unlock and delete files or folders that are being held by a process or are otherwise locked by the system.
Spread this all-sided strategy of deleting across the following social media.
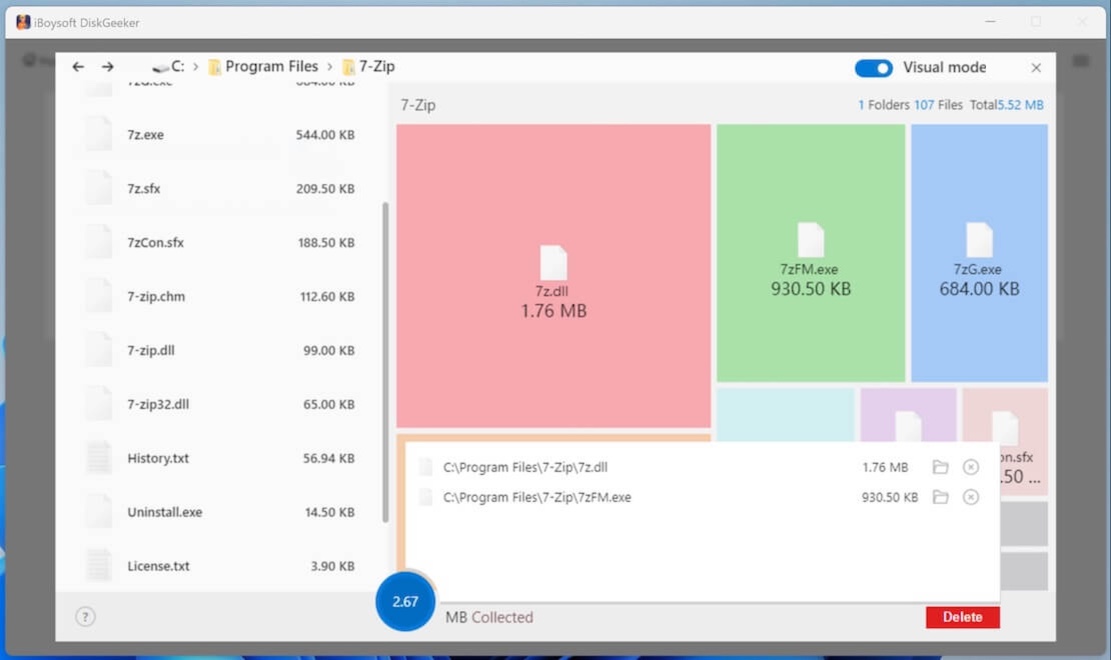
How to use iBoysoft DiskGeeker to delete files/folders
Files filling up your computer or hard drive can slow down performance. Unlike traditional Windows deletion methods, iBoysoft DiskGeeker for Windows quickly locates large files and folders across your system, offering both visual and non-visual views of disk usage.
With a simple drag-and-drop, it permanently removes unnecessary files—images, documents, videos, and more—freeing up space instantly. Standard deletion methods often leave residual data, consuming more space. Have a trial with the following guide to have a wonderful deletion:
Tuturiol to analyze the space of a partition or folder and clean files
Its Space Analyzer function is designed to quickly find the large files and folders in the system partition or target folder so as to clean up a PC or external hard disk and release more free space.
Step 1: Click the following green button to download and launch the iBoysoft DiskGeeker for Windows.
Step 2: Space analyzer module presents itself.
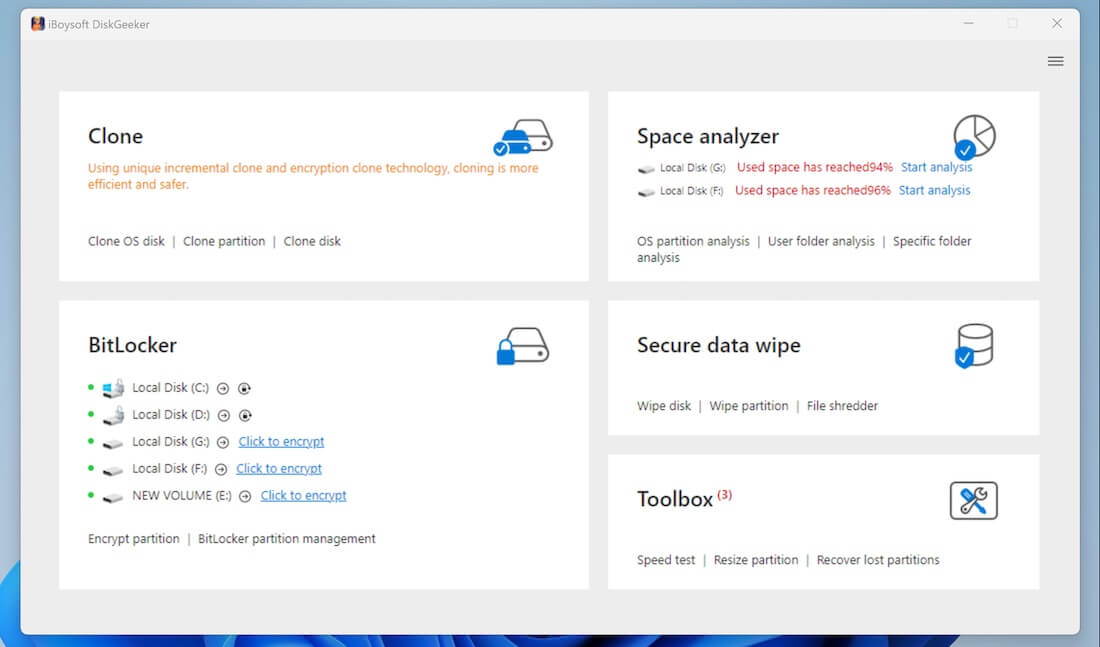
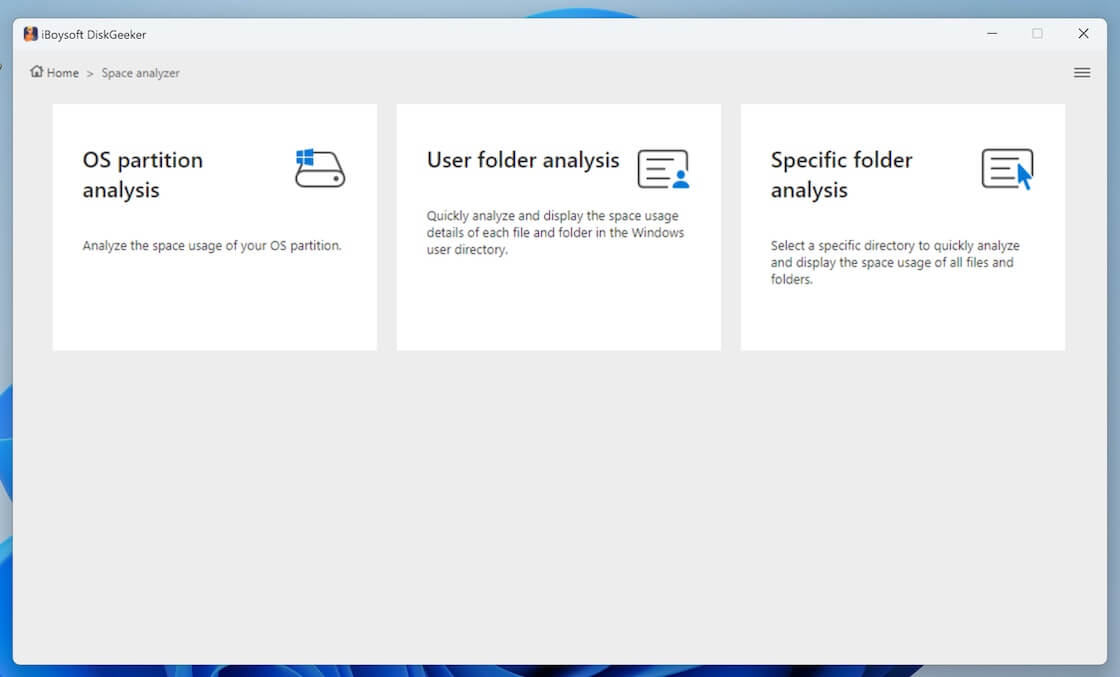
Step 3: Click "OS partition analysis," "User folder analysis," or "Specific folder analysis" from the Space analyzer module.
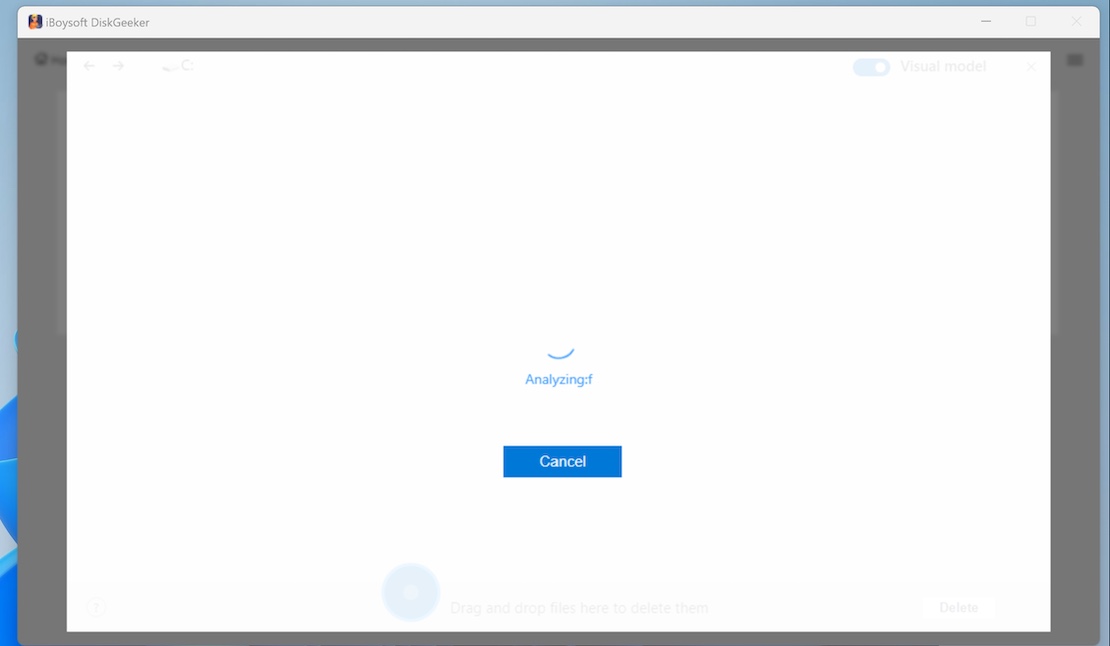
Step 4: iBoysoft DiskGeeker for Windows will automatically analyze the files in the selected location. (It will take a relatively long period to scan the files in OS partition and user folder as it stores a huge amount of your data.)
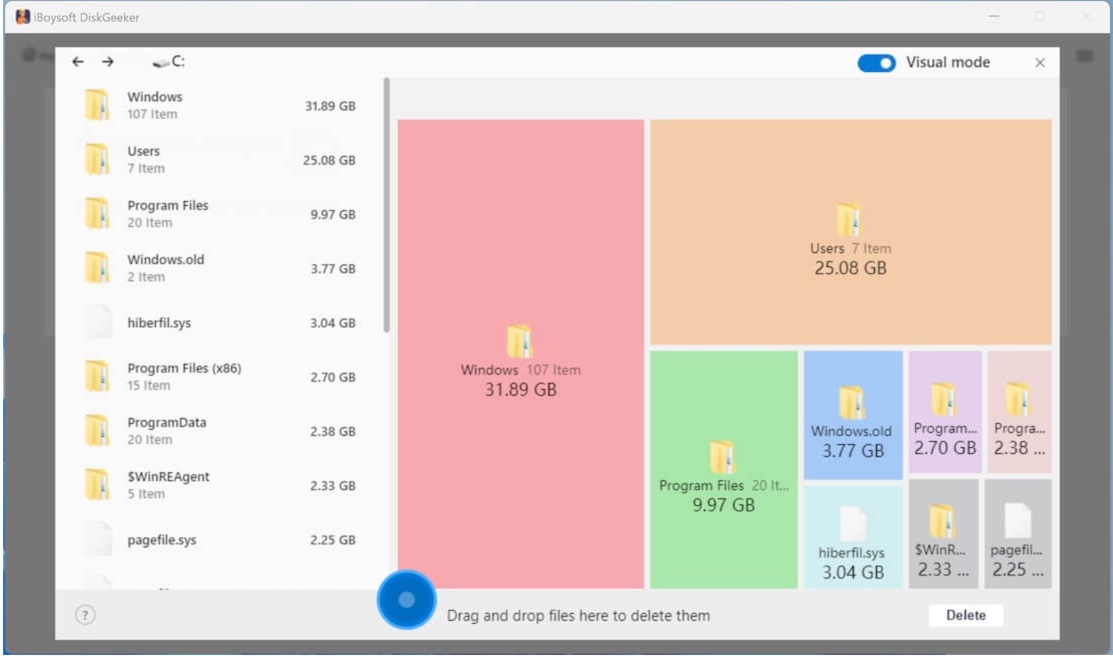
Step 5: Check the scanned results by clicking the listed folders. (The scanned results can be displayed in two modes: Visual mode and Non-visual mode.)
In visual mode, the left and right views are the same level directories, and the right view is a visual presentation of the files in the left view. Turn off the Visual mode button in the upper right corner, you can only see the text table of contents.
In non-visual mode, the software displays the preceding and following levels of directories of the current path (a total of three levels of directories). When there are less than three levels of directory structure, it displays all path structures.
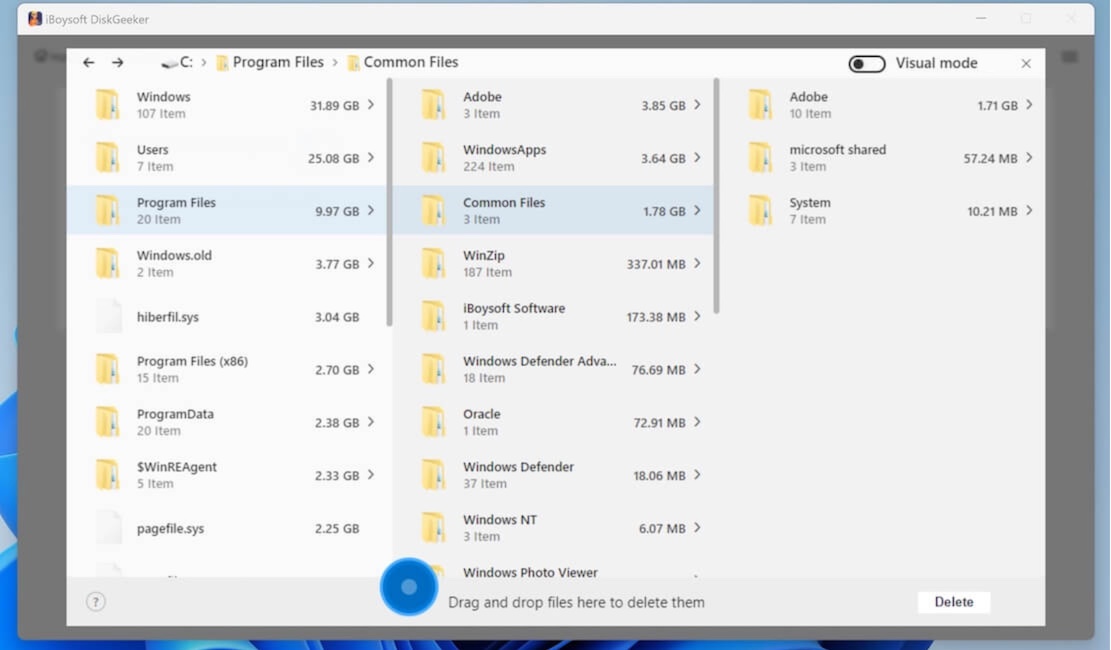
Step 6: Select your unwanted files and drag and drop them to the Trash Bin (blue circle) at the bottom of the window (the blue circle collects all the files you prepare to delete, and it will show the total size of these files.
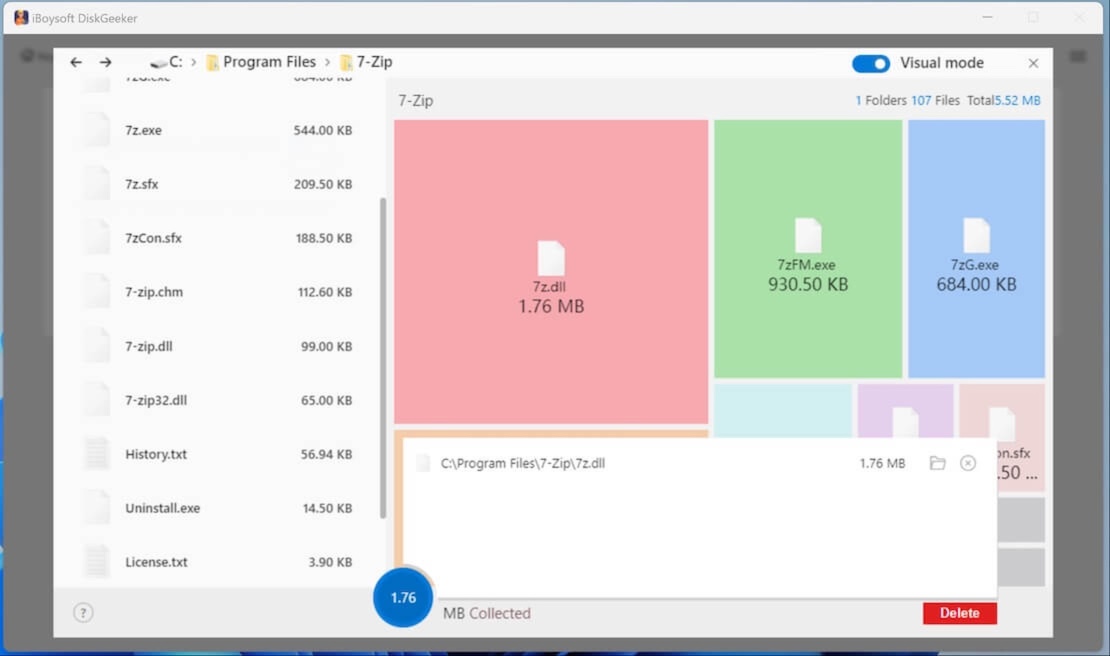
If you regret moving a certain file to the blue Trash Bin, you can click on the Trash Bin and then click the Remove (X) button next to the file to move it out from there.
Step 7: Click "Delete" to permanently remove the files.
Note: A prompt will appear if the deletion is successful. Remember to refresh that folder to show the latest state. Also, it will notify you when a deletion failure happens. You can click the file path on the pop-up to open the file and find the reasons. Usually, a read-only file and file being used cannot be deleted.
Conclusion
In Windows 10/11, deleting files, folders, or directories is usually a straightforward task, but issues can arise that prevent normal deletion. By understanding the different methods available—normal and forceful, you can handle even the most stubborn items.
Normal methods like using File Explorer or the Command Prompt work well for most common deletion scenarios. Forceful methods, such as using PowerShell, Safe Mode, or third-party tools, are useful when files or folders are locked, protected, or in use.
All in all, if you want to spare your effort to delete files rapidly and carelessly, use iBoysoft DiskGeeker for Windows, you should be able to readily delete large amounts of files, folders, or directories in Windows. Share these insights and never be bothered by deleting file rejections and file remnants.
Related articles
How to Uninstall Programs in Windows 10 in Seven Ways
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Install Apps on Windows 7/10/11
How to Fix Common BitLocker Recovery Issues in Windows
How to Screenshot on Windows 10/11 in Six Ways
