Written by
Yuri ZhangSummary: This post elaborates on VBS, an advanced security feature that leverages hardware virtualization to isolate critical parts of the system. iBoysoft DiskGeeker offers a more effortless way to protect your data with its BitLocker.
Do you have any idea of VBS? Don't miss this critical feature in modern Windows operating systems, designed to safeguard against a variety of cyber threats. Now let's delve into Virtualization-Based Security (VBS) by definition and how to enable or disable it.
What is Virtualization-Based Security (VBS)?
Virtualization-Based Security (VBS) in Windows utilizes hardware virtualization features such as Intel VT-x or AMD-V to create a secure, isolated environment within the system. This secure environment is used to protect crucial parts of the operating system, including Credential Guard, Device Guard, and Hypervisor-Protected Code Integrity (HVCI). These features are designed to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data, even in the event of a malware attack or system compromise.
VBS works by creating a Virtual Secure Mode (VSM), which isolates critical system processes and data from the rest of the OS. This makes it difficult for malicious software to access sensitive information, providing an added layer of defense against advanced attacks.
Key features of VBS in Windows
VBS helps ensure that even if an attacker gains control over the operating system, the isolated areas remain protected.
- Hypervisor-Protected Code Integrity (HVCI): It helps protect against malware that attempts to inject itself into the kernel or load unsigned drivers.
- Credential Guard: Credential Guard is a feature of VBS that uses virtualization to protect user credentials, such as NTLM hashes and Kerberos tickets, from being stolen by attackers.
- Device Guard: It blocks the execution of untrusted or malicious code, ensuring that only approved applications and drivers can run.
- Windows Defender System Guard: System Guard is a set of features that protect the system from attacks during the boot process, ensuring that the operating system kernel and other critical components are not tampered with.
- Measured Boot: Measured Boot works in conjunction with Secure Boot and records the system's boot process in a log. VBS helps to protect this log to ensure that the integrity of the boot process remains intact.
Enabling VBS in Windows
VBS is typically enabled through the Windows Security settings or Group Policy for enterprise environments. It may also be automatically turned on in certain system configurations, such as with Windows 10/11 Enterprise or Pro editions that have advanced security settings. To enable VBS manually:
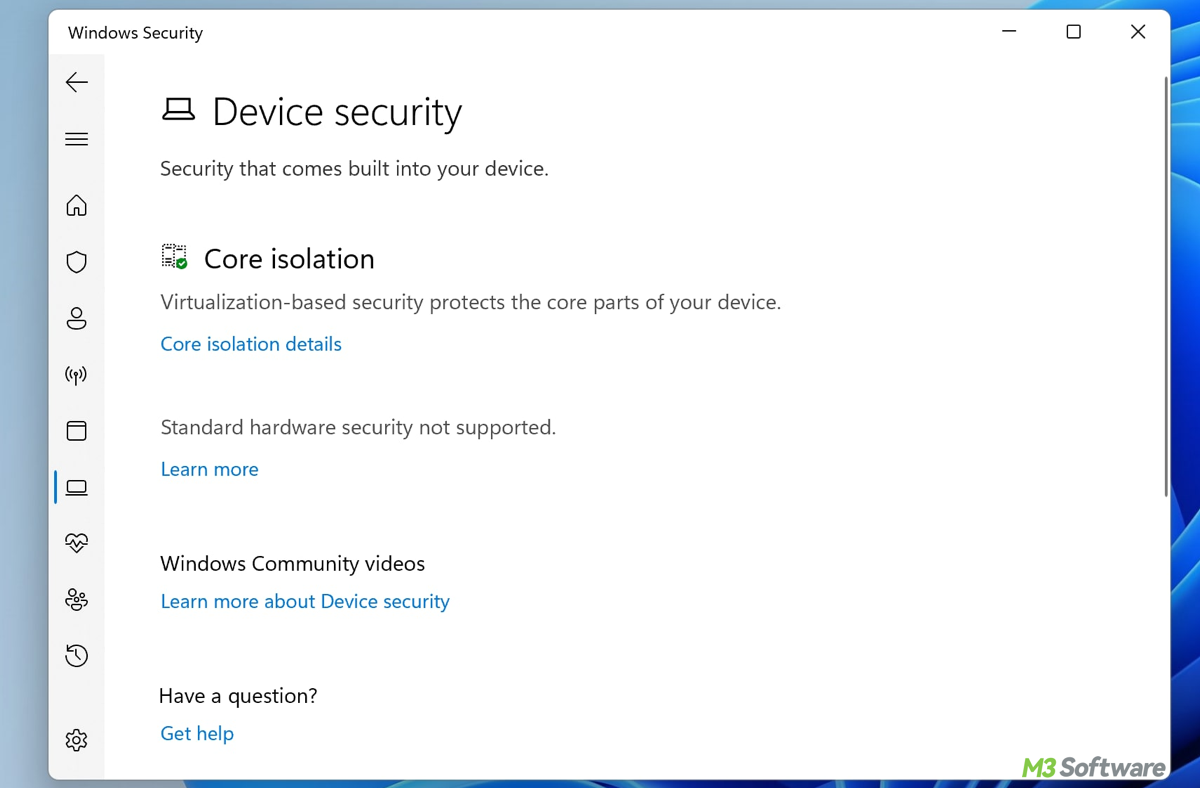
- Go to Settings > Windows Security > Device Security > Core Isolation.
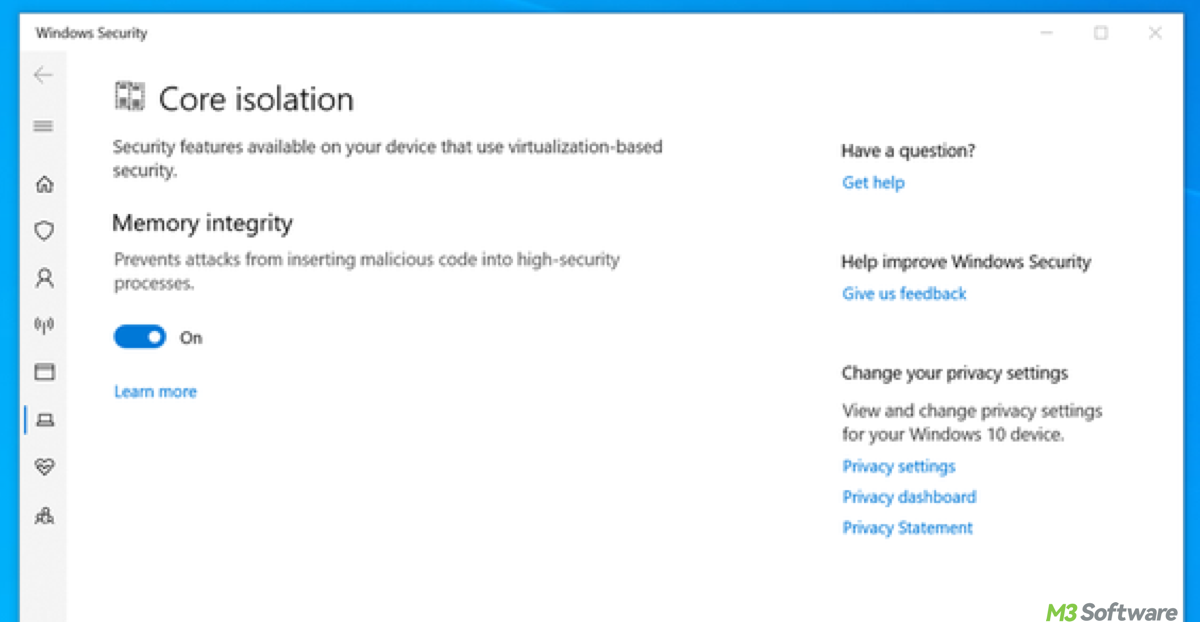
- Enable the Memory Integrity option (HVCI).
- Optionally, you can enable Credential Guard through Windows Defender Security Center.
You can also enable VBS by running certain PowerShell commands or through BIOS/UEFI settings to ensure that virtualization is supported and enabled at the hardware level. Need more details about this, share and contact us!
Disabling VBS in Windows
Disabling Virtualization-Based Security (VBS) on a Windows machine may be necessary in some situations, such as when troubleshooting compatibility issues with certain hardware or software. However, it's important to note that disabling VBS reduces the security posture of the system, as it removes the protections that VBS provides, like Credential Guard, Device Guard, and Hypervisor-Protected Code Integrity (HVCI).
If you still wish to proceed, here are the steps to disable VBS in Windows:
- Press Windows + I to open Settings.
- Navigate to Privacy & Security > Windows Security > Device Security.
- Under Core Isolation, click on Core Isolation Details.
- Turn off Memory Integrity (which is part of HVCI). This may automatically disable VBS as well.
- Restart your computer to apply the changes.

Conclusion:
Virtualization-Based Security (VBS) in Windows provides a significant security enhancement by isolating key parts of the system using hardware-assisted virtualization. It helps protect against attacks that target sensitive data, credentials, and the operating system kernel, providing robust defense mechanisms like Credential Guard, Device Guard, and HVCI. Although it requires specific hardware support and may introduce a slight performance impact, the security benefits it offers make it an essential feature for protecting modern Windows systems.
Related articles
Microsoft/Windows Defender for Everyone
How to Turn Off Windows Defender Swiftly
Understanding & Enabling Windows Defender Application Guard
If you don't want other expertise to slip, share and comment!
