Written by
Yuri ZhangSummary: This article explains what GPO BitLocker is, including BitLocker GPO settings. We also offer detailed tutorials to configure GPO, turn on or disable BitLocker via GPO, and so on. Use BitLocker in iBoysoft DiskGeeker if you think GPO is hard to master.
BitLocker Drive Encryption provides a strong solution for protecting sensitive information on Windows. Utilizing Group Policy Objects (GPO) in conjunction with Active Directory (AD) enhances the management and enforcement of BitLocker settings across an organization.
Let's dive into the key aspects of GPO BitLocker settings, focusing on its functionality, including recovery key management, USB settings, and how to enable or disable BitLocker without TPM via GPO, as well as configure PIN settings.
What is GPO BitLocker and its features?
GPO BitLocker refers to the integration of BitLocker Drive Encryption with Group Policy Objects (GPO) in a Windows Active Directory environment, enabling centralized management of data protection across multiple devices.
This powerful tool allows IT administrators to enforce consistent encryption policies, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure from unauthorized access. With GPO BitLocker, organizations can easily configure various settings, such as recovery key management, authentication methods, and encryption algorithms, tailored to their security needs.
Additionally, it facilitates the encryption of both internal drives and removable USB devices, while also providing options for unlocking drives using PINs or passwords. Even without TPM, GPO facilitates consistent policy enforcement across devices.
Note: Unlike normal BitLocker relies on individual device configurations, which are manual and limited, GPO BitLocker provides centralized, consistent management of BitLocker settings.
Overview of GPO BitLocker settings
GPO BitLocker settings enable centralized management of BitLocker configurations, allowing administrators to enforce policies for:
- Apply BitLocker encryption to operating system drives and fixed data drives.
- Configure unlock options, such as passwords, PINs, or USB keys.
- Automatically store recovery keys in Active Directory, facilitating quick recovery of encrypted drives when users forget passwords.
Tips: GPO also includes specific configurations or settings for USB drives. Administrators can enforce BitLocker encryption on USB drives, ensuring data protection. Similar to other drives, recovery keys for USB drives can be stored in Active Directory, and policies can dictate how users unlock their encrypted USB drives.
Share this if you find it helpful.
How to manage BitLocker with GPO in Active Directory
The primary goal of configuring GPO for BitLocker is to establish consistent encryption policies across all devices within an organization. This not only enhances data security but also simplifies management tasks for IT administrators.
How to configure GPO for BitLocker in Active Directory
These steps also enable BitLocker via GPO:
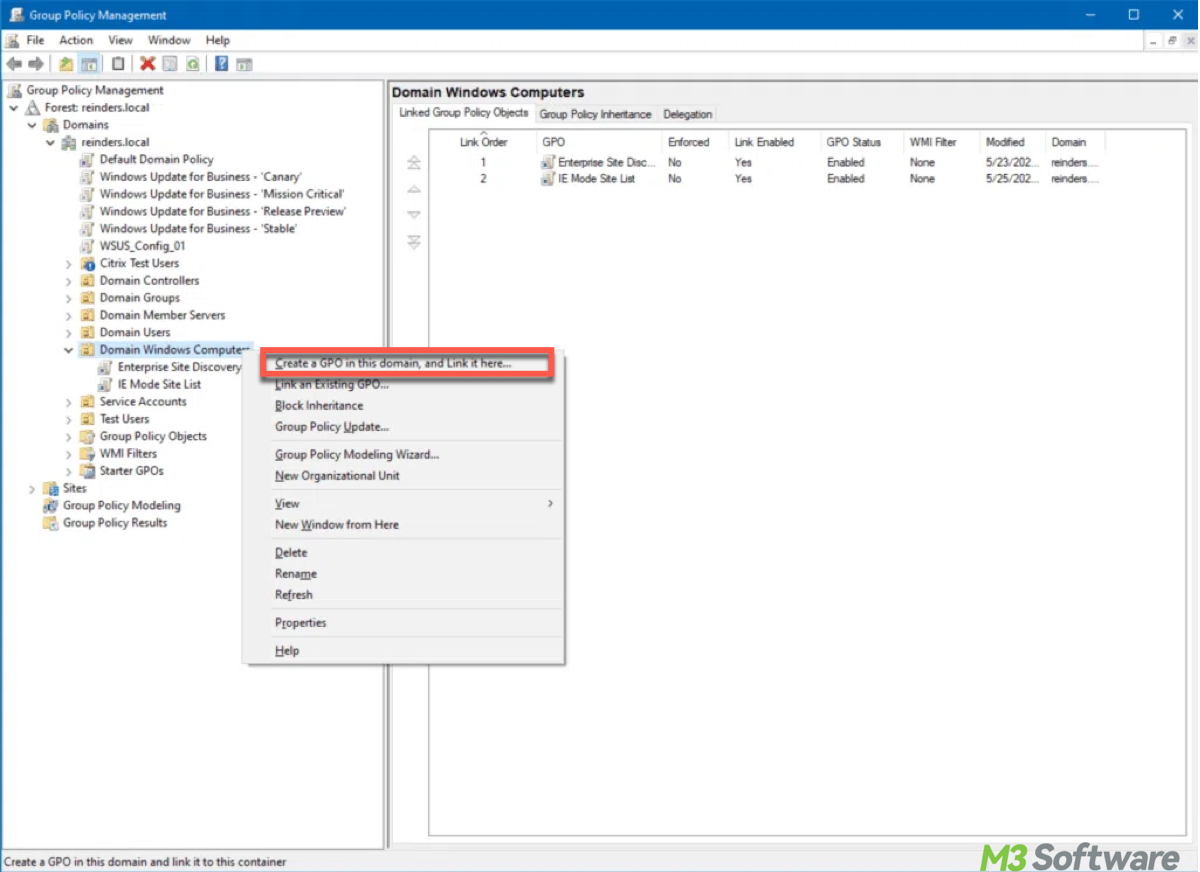
- Press Win + R, type gpmc.msc, and hit Enter. This opens the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC).
- To create or edit a GPO linked to the appropriate OU, in the GPMC, right-click the appropriate Organizational Unit (OU) where you want to apply BitLocker settings, then select "Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here..." or choose an existing GPO to edit.
- To go to BitLocker settings, go to Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > BitLocker Drive Encryption in the Group Policy Management Editor.
- Set Recovery Key Storage to specify how recovery keys will be stored in Active Directory to facilitate recovery if needed.
- Ensure the GPO is linked and applied to the desired OU containing the computers you want to enforce the settings on.
- On client machines, run gpupdate /force in the command prompt to apply the new policy immediately, or wait for the next automatic Group Policy refresh.

Tips: Here's how to run gpupdate /force command: Press Win + R, type cmd, and press Enter, then type gpupdate /force and press Enter to refresh Group Policy settings immediately.
How to turn off BitLocker via GPO
To disable BitLocker through GPO, follow these steps:
- Access the GPMC: Open it as described above.
- Choose the GPO you want to modify.
- Go to the BitLocker Drive Encryption settings.
- Enable the setting to prevent users from enabling BitLocker on specified drives.
- Ensure GPO is linked to the appropriate OU.
- Update Group Policy by using gpupdate /force command to apply changes.
Tips: For existing encrypted drives, manual decryption may be required since GPO does not manage decryption directly.
How to enable BitLocker without TPM via GPO
For organizations without Trusted Platform Module (TPM) hardware, BitLocker can still be enabled through GPO. Administrators can configure settings to allow:
- Press Win + R, type gpmc.msc, and hit Enter. This opens the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC).
- Right-click on the desired organizational unit (OU) and select "Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here..." or edit an existing GPO.
- Right-click the GPO and choose "Edit."
- Go to Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > BitLocker Drive Encryption.
- Under "Operating System Drives", double-click "Require additional authentication at startup."
- Enable the setting and check the option for "Allow BitLocker without a compatible TPM". This allows you to use a password or USB key instead.
- Ensure the GPO is linked to the appropriate OU for the computers where you want to enforce these settings.
- Use gpupdate /force on client machines to apply the new policy, or wait for the next Group Policy refresh.
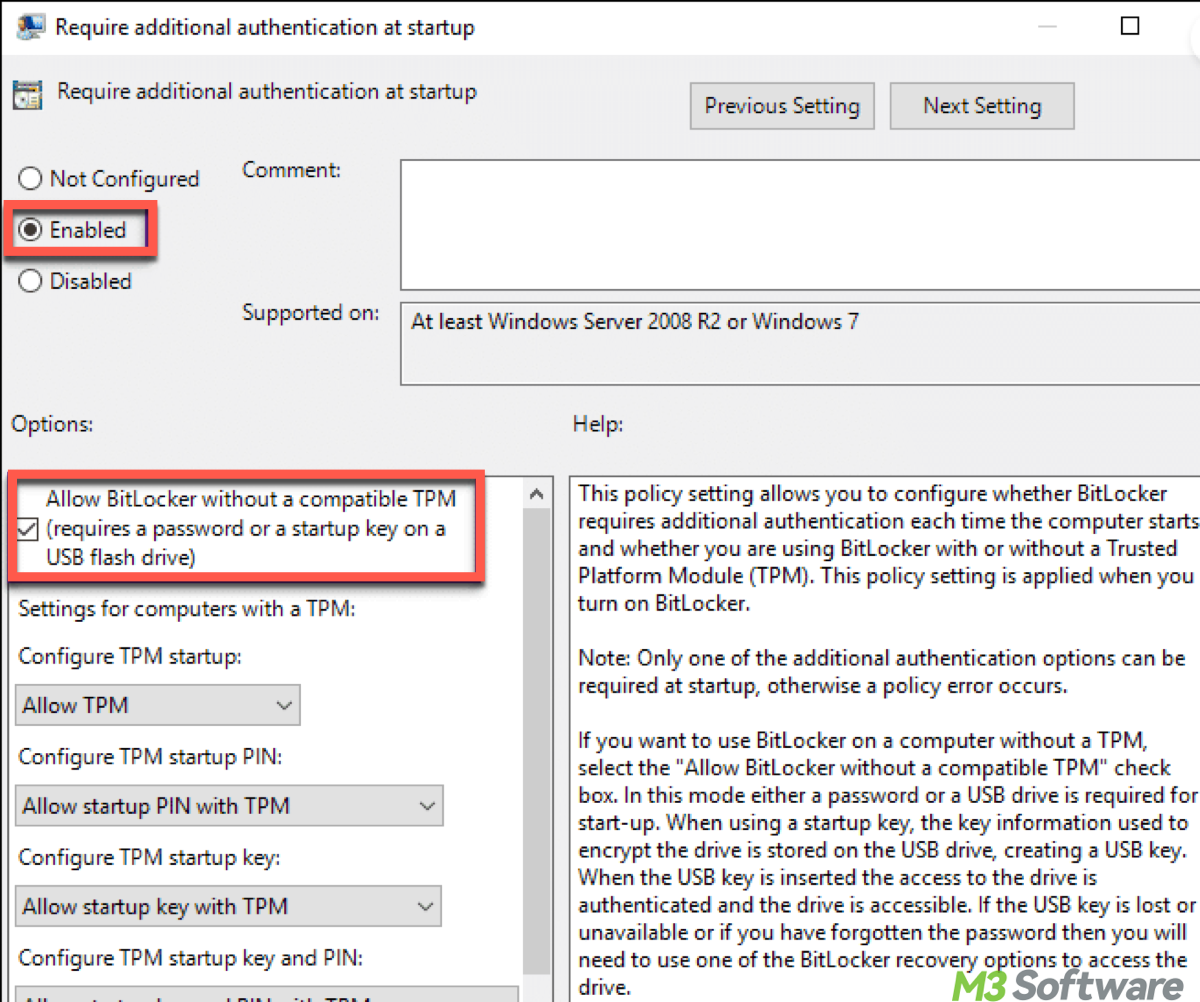
Note: Without TPM, users will need to enter a password or insert a USB key each time they start their device to unlock the drive. While using BitLocker without TPM is feasible, it may be less secure than using TPM, as the encryption keys are stored on the drive itself rather than securely within the TPM chip.
How to configure BitLocker PIN length through GPO
The length and complexity of a BitLocker PIN can also be managed through GPO, to set these parameters:
- Open GPMC as mentioned and edit the relevant GPO.
- Navigate to BitLocker Settings and select "Require additional authentication at startup."
- To adjust PIN requirements, set the minimum length (typically at least 6 digits) and the maximum length (up to 20 digits).
Conclusion
Integrating BitLocker management with Group Policy Objects in Active Directory provides a comprehensive approach to data security. By centralizing encryption settings, recovery key management, and USB drive policies, organizations can protect sensitive information effectively while simplifying administrative tasks, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, and streamlining recovery processes.
Also read How to Use BitLocker with Ease
Share this with someone who needs to use GPO BitLocker in following social media.
