Written by
Wilsey YoungSpeaking of data encryption features on Windows, EFS (Encrypting File System) and BitLocker are the two common options on a Windows computer. Although both serve the same purpose of protecting your precious data, they work in different ways and suit diverse situations.
This post revolves around EFS vs BitLocker and mainly discusses the main differences between Windows EFS encryption and BitLocker encryption features.
What is the EFS (Encrypting File System) feature on Windows?
Encrypting File System (EFS) is a built-in feature in Windows that allows you to encrypt individual files and folders on an NTFS-formatted drive. EFS is designed to protect your sensitive data from unauthorized access and potential leakage. With the help of EFS, you can choose specific files or directories to encrypt, and only authorized users can decrypt and access the encrypted content.
How does EFS (Encrypting File System) work?
Once the EFS is enabled on a file or folder, the Windows system generates a unique symmetric encryption key called the File Encryption Key (FEK) for that particular file. This File Encryption Key is exclusively used to encrypt the file's data using a symmetric encryption algorithm, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard).
Once the file is encrypted, the FEK itself is encrypted with the user's public key (from the user's EFS certificate) and stored along with the file.
EFS relies on user authentication to ensure that only authorized users can access encrypted files. When the user logs in, Windows decrypts the encrypted FEK using the user's private key, allowing access to the encrypted file. The private key is automatically generated when a file is encrypted using EFS and is tied to the user account that performed the encryption.
Conversely, if another user uses the improper EFS certificate to access the file, they will not be able to decrypt the FEK, and the file remains inaccessible.
You can click the buttons below to share the post!
EFS vs BitLocker: What are the differences?
Both EFS and BitLocker provide encryption, but they differ in some aspects that are crucial for beginners to understand.

EFS vs BitLocker: Encryption scope
EFS encrypts individual files and folders, while BitLocker encrypts entire drives or specific partitions. EFS boasts more flexibility, and BitLocker suits you more when it comes to securing an entire volume.
EFS vs BitLocker: Compatibility
EFS is available in most versions of Windows OS, while BitLocker is only available on Pro, Enterprise, and Education editions of Windows, such as Windows 11/10 Professional, Enterprise, and Education editions, Windows 8/8.1 Professional and Enterprise editions, Windows 7 Enterprise and Ultimate editions.
EFS vs BitLocker: Limitation
EFS (Encrypting File System) is compatible only with NTFS-formatted drives, which means you can only encrypt individual files or folders on an NTFS-formatted drive. BitLocker relies on a TPM (Trusted Platform Module) chip to maximize the effect.
EFS vs BitLocker: Target User
EFS is useful when files are stored on a Windows system with different users. This is because EFS is connected to the user, not the machine, so users can have their files encrypted without worrying about unauthorized access from others.
BitLocker plays a more important role in protecting data on lost or stolen devices, even when your device is improperly decommissioned. It secures the entire drive or a specific partition.
EFS vs BitLocker: Security Model
EFS relies on user credentials (password or key), and the encrypted files are tied to the Windows user account. BitLocker uses a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) to secure the entire volume and can integrate with other authentication methods like PINs or USB keys.
How to enable Encrypting File System?
After understanding EFS vs BitLocker, you can follow these steps to encrypt a file or folder using EFS if you want to:
- Open File Explorer and right-click on the file or folder you want to encrypt
- Choose "Properties."
- Click the "Advanced" option.
- Tick the checkbox of "Encrypt contents to secure data."
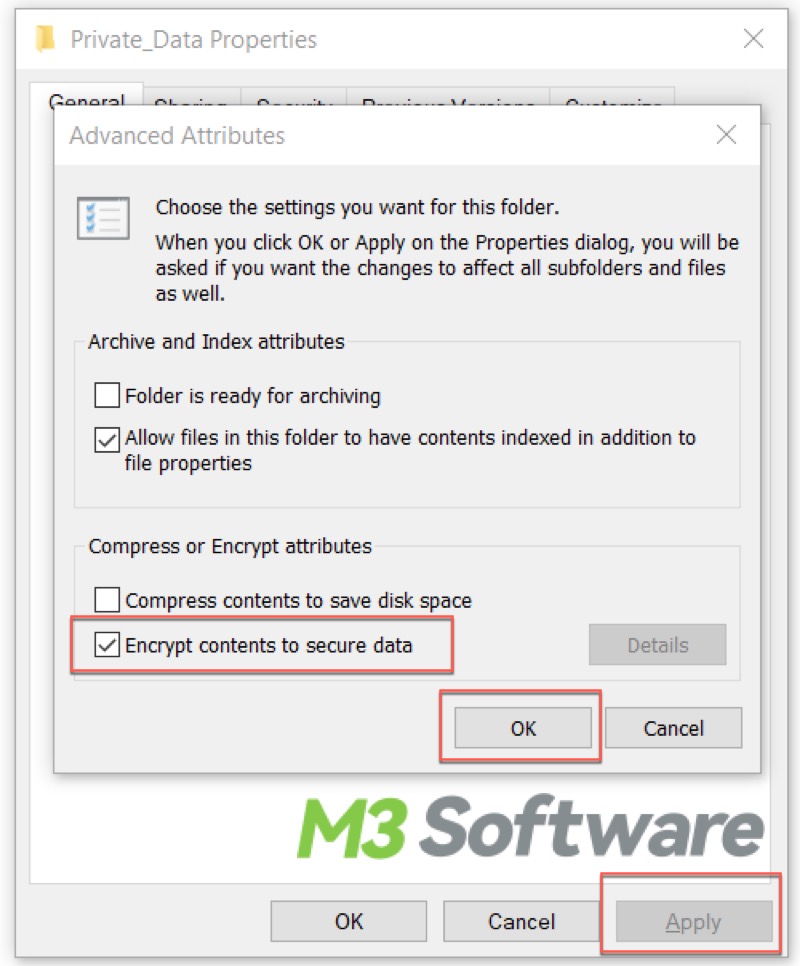
- Click "OK."
- Click "Apply" to let the change take effect.
- A window will pop up to ask if you want to encrypt the selected folder or the folder, subfolder, and its files
- Click the option according to your needs and then click "OK."
- When you see a small padlock icon on the file encrypted with EFS, it means EFS is successfully enabled.
Conclusion
By clearly understanding the differences between EFS and BitLocker encryption, you can choose the encryption method that suits you the best, whether it's for securing specific files or an entire drive.
Do you find this post helpful? You can share with your friends!
