Written by
Wilsey YoungSummary: This post revolves around Clean Boot vs Safe Mode on Windows, discussing what they are, how they work, and the main differences between them. -From m3datarecovery.com

Clean Boot and Safe Mode, the built-in troubleshooting tools on Windows, can help identify and fix issues, including errors, system crashes/freezes, performance slowdown, or other problems that make your Windows PC act up.
Many users may confuse Clean Boot with Safe Mode, as they seem to function similarly. Therefore, understanding the Clean Boot vs Safe Mode is essential for us to make the right choice when a problem or error appears.
You can click the buttons below to share this post
Clean Boot vs Safe Mode: Overview
Clean Boot is a diagnostic mode on Windows that boots up the system without non-essential third-party apps, programs, and services.
Safe Mode is a startup mode that starts up Windows by loading the essential files, drivers, and services needed for the operating system to run.
Clean Boot vs Safe Mode: Purposes
Clean Boot allows you to identify third-party software, apps, or programs that might lead to the problems. In other words, when Clean Boot is enabled, you will know whether the issue or glitch on Windows is caused by certain apps or services or the conflicts between them.
Safe Mode makes it easier for you to isolate problems triggered by corrupted files, defective drivers, or malware running in the background etc.
Clean Boot vs Safe Mode: Appearance
Under the Clean Boot, Windows looks and behaves normally but with fewer processes running in the background. Functionality is not limited, making it more flexible and closer to normal use.
Under the Safe Mode, the user interface is basic, and the display resolution is seemingly low. Features are limited, so the system environment is more restrictive.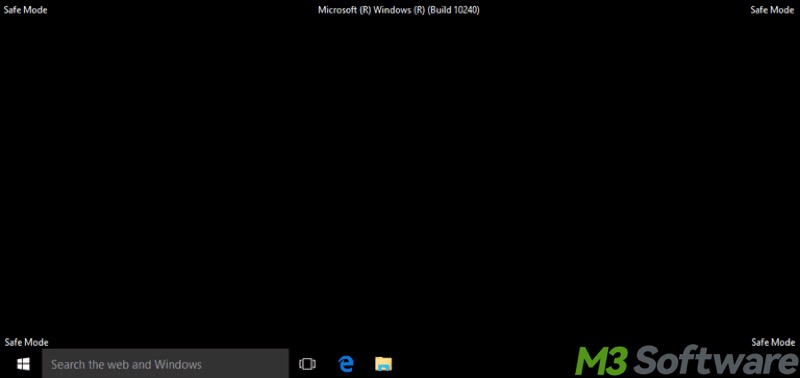
Clean Boot vs Safe Mode: Which one to choose
Clean Boot is helpful when:
- You suspect an installed third-party app or program is causing the problem.
- You want to isolate software conflicts.
- System startup or performance is slow, and you want to identify which startup app or service is the culprit.
Safe Mode is recommended when:
- Windows cannot boot up normally, such a BSOD (Blue Screen of Death).
- You want to uninstall or disable malware, software, or drivers that trigger the issue.
- You want to perform a system restore to revert the system to a previous state.
Clean Boot vs Safe Mode: How to perform
Here's how to enter the Clean Boot on Windows:
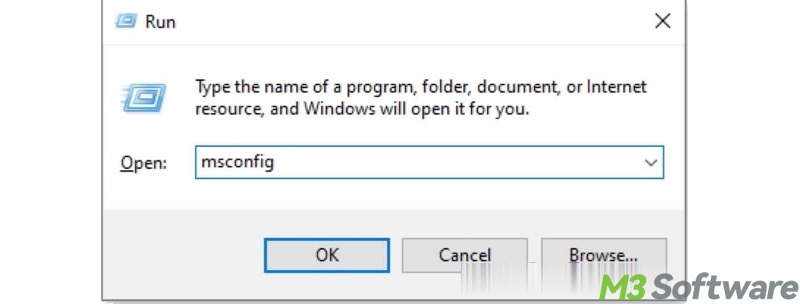
- Press the Windows+R keys to open the Run dialog box.
- Type msconfig in the box and hit the Enter key on your keyboard to open the System Configuration window.
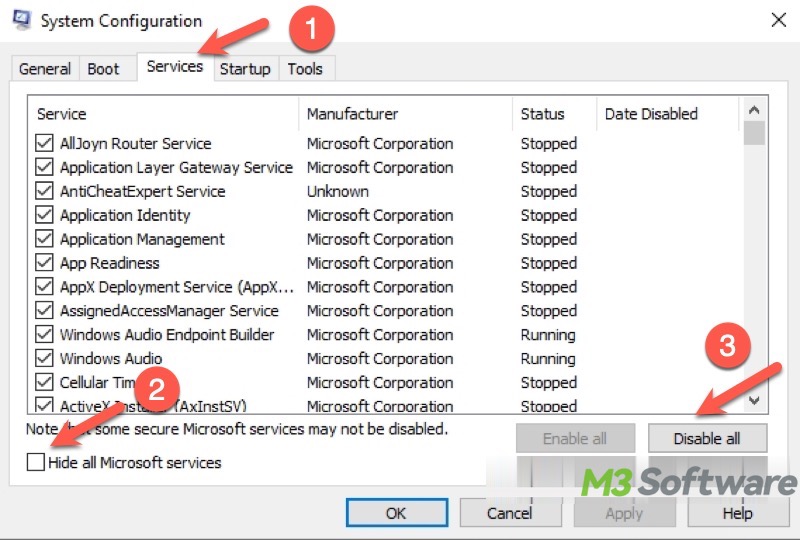
- Go to the Services tab and tick the checkbox "Hide all Microsoft services."
- Click the "Disable all" button to disable all non-essential services.
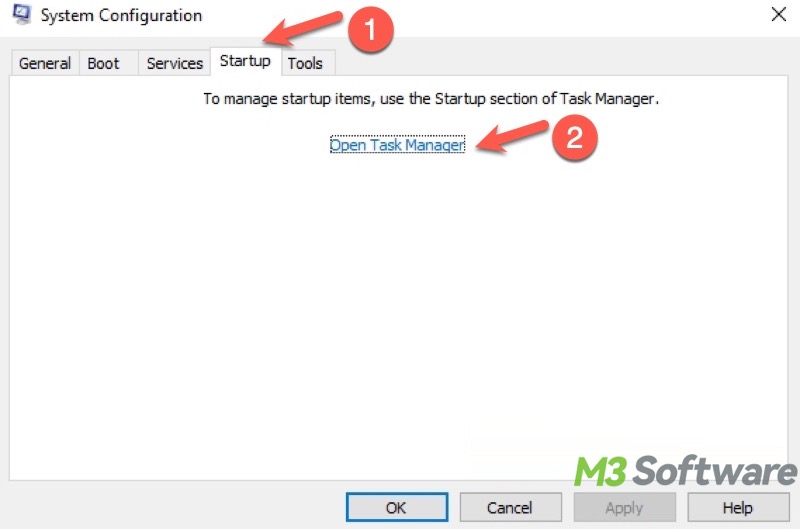
- Go to the Startup tab and tap on Open Task Manager.
- Under the Startup tab of Task Manager, disable all the listed startup apps and programs, then close Task Manager.
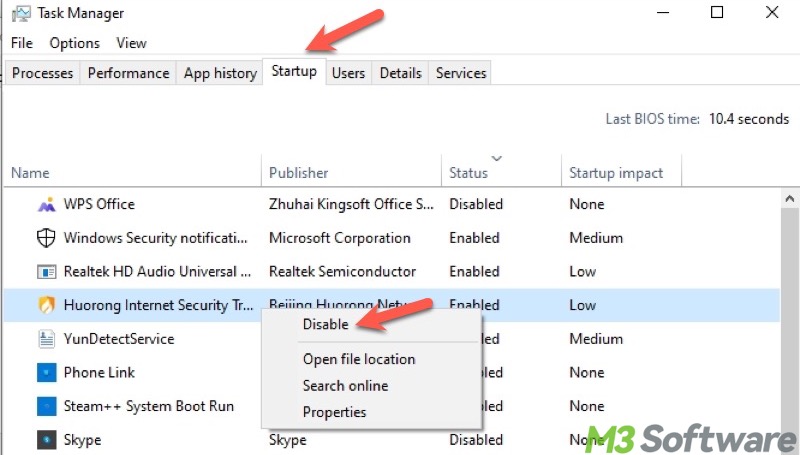
- Click the Apply and OK buttons under System Configuration, and you'll be prompted to restart the PC, and the system will boot into Clean Boot automatically.
To exit the Clean Boot mode:
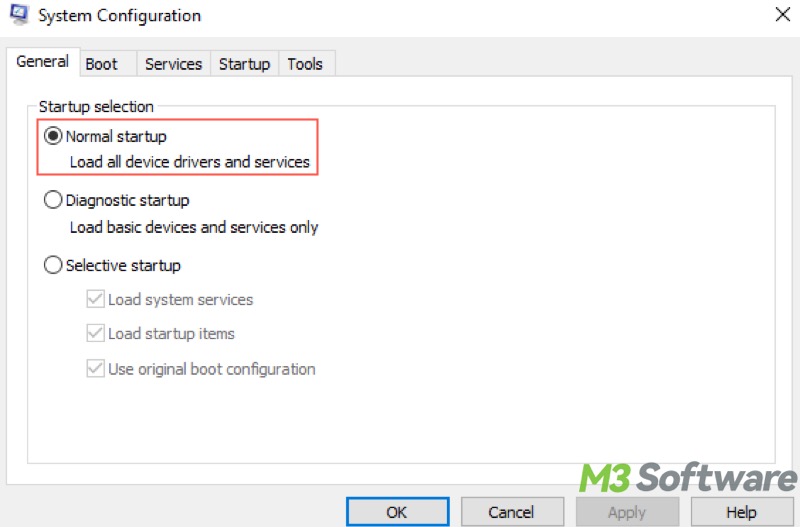
- Open the System Configuration window.
- Under the General tab, ensure “Normal startup” is selected.
- Under the Services tab, uncheck "Hide all Microsoft services" and click the "Enable all" button.
- Open Task Manager to enable the startup programs you want.
Here's how to boot your system into Safe Mode:
- Press the Windows + R keys to open the Run dialog box.
- Type msconfig in the box and press the Enter key to open the System Configuration window.
- Go to the Boot tab, select Safe Boot, and choose Minimal (Standard Safe Mode).
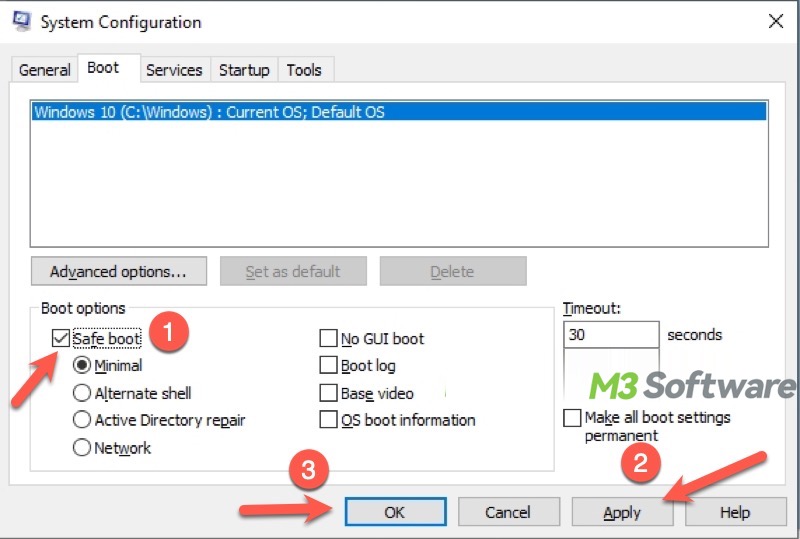
- Click Apply, OK, and restart your PC.
Alternatively, if your PC cannot start normally, enter Safe Mode through WinRE (Windows Recovery Environment):
- Power on your Windows PC. Once you see the Windows or manufacturer logo pop up, press and hold the power button until the computer powers off.
- Repeat the process above 2-3 times, and Windows should boot into Safe Mode automatically.
- Choose Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings.

- In the Startup Settings page, press the F4 key on your keyboard to choose Safe Mode.

- Windows will boot into Safe Mode automatically.
To exit Safe Mode, open the System Configuration window, uncheck “Safe boot” under the Boot tab, click Apply and OK, and restart your PC.
Conclusion
Understanding Clean Boot vs Safe Mode can save you a lot of trouble when the system runs into issues. Clean Boot will be ideal if you want to identify and fix conflicts or issues caused by third-party apps and services. If your PC encounters serious problems, such as startup failures or system corruption, Safe Mode offers a more secure environment for troubleshooting.
Share this post with your friends if you find it helpful
